ID:
5yo girl brought to the pediatric emergency department by her mother due to 3 days of fever.
HPI:
The patient’s fever was first noted 3 days ago, measured at home to 103°F. It is associated with a moist cough, vomiting, and decreased PO intake. Her mother reports that she appears lethargic and has been urinating less frequently. The patient denies headache, changes in vision, burning with urination, or ear pain. No known sick contacts, attends day care.
PMH (Birth History):
No significant medical/surgical history. Ex-term born NSVD with no complications.
PE:
- VS: 95/65mmHg, 100bpm, 102.6°, 22/min
- General: Well-appearing, mildly irritated but consolable
- HEENT: NC/AT, PERRL, oropharynx without erythema, no cervical LAD
- CV: RRR, no M/G/R
- Lungs: No evidence of respiratory distress (retractions, flaring), faint crackles over right inferior lung fields
- Abd: +BS, soft, non-distended, TTP RLQ > LLQ, no rebound/guarding
- Back: No CVAT
Labs/Imaging:
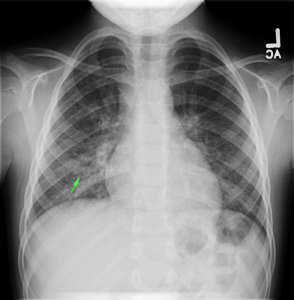
- CXR PA/Lateral: RML/RLL infiltrate
Assessment:
5yo with 3 days persistent high fever and cough. These symptoms along with examination findings of crackles warranted further imaging (CXR) which revealed infiltrate in the right inferior lung field. The patient appeared clinically stable and was tolerating PO intake in the ED and was discharged home with azithromycin 5mg/kg/dose (with loading dose), clinic follow-up and strict return precautions.
Evaluation and Management of Pediatric Fever
A System for Pediatric Fever:
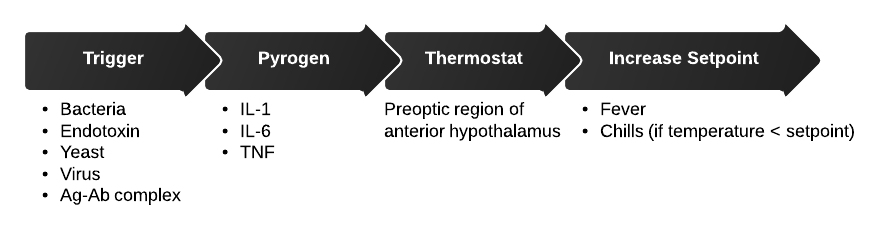
Pathophysiology:
Diagnosis:
- <3mo: 38.0°C, 100.4°F
- 3-36mo: 39.0°C, 102.2°F
- Rectal > oral > axillary
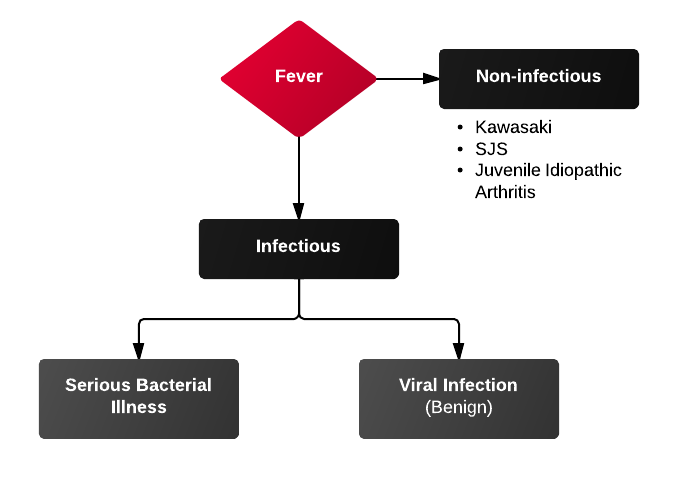
Differential Diagnosis of Pediatric Fever:
Serious Bacterial Illness (SBI):
1) UTI and pyelonephritis
- Most common cause of SBI
- Accounts for 3-8% of uncharacterized fevers
- Female > male, uncircumcised > circumcised
- Consider BCx, CSF evaluation as 5-10% bacteremic at presentation
- Urinalysis: LE 75% specificity, Nitrites 97% specificity
2) Pneumonia and sinusitis
- Sinusitis uncommon <3yo (sinuses unformed)
- PNA diagnosed with CXR, obtain if findings of respiratory distress (grunting, tachypnea, hypoxemia) or rales on exam
3) Meningitis
- Diagnose with LP
- Meningitis suggested if:
- ANC > 1,000
- Protein > 80
- Seizure (particularly complex febrile seizure)
Diagnosis by Age Group:
<3mo
- Physical exam findings:
- Tachypnea, hypoxemia → LRT infection
- Irritability, inconsolability, bulging anterior fontanelle → meningitis
- Vomiting/diarrhea → non-specific, GE, AOM, UTI, meningitis
- History
- Recent immunization: increased risk of SBI (usually UTI) 24-72h after immunization
- Confirmed bronchiolitis (viral): enterovirus/parainfluenza associated with SBI
3-36mo
- Physical exam findings:
- Viral (URTI, GE) → vomiting, diarrhea, rhinorrhea, cough, rash; still playful and responsive
- UTI → fever, foul-smelling urine, crying when urinating
- Meningitis → irritability with handling, vomiting, bulging anterior fontanelle, complex febrile seizures
>36mo
- Physical exam findings: presentation more adult-like
- Watch for:
- Group A Streptococcal pharyngitis
- Infectious mononulceosis
- Kawasaki: high fever (>5d), strawberry tongue, conjunctivitis, desquamating rash on palms/soles


Pingback: Acil Tıp Uzmanının Çocuk Hastayla İmtihanı - 1 - Acilci.Net