Imaging
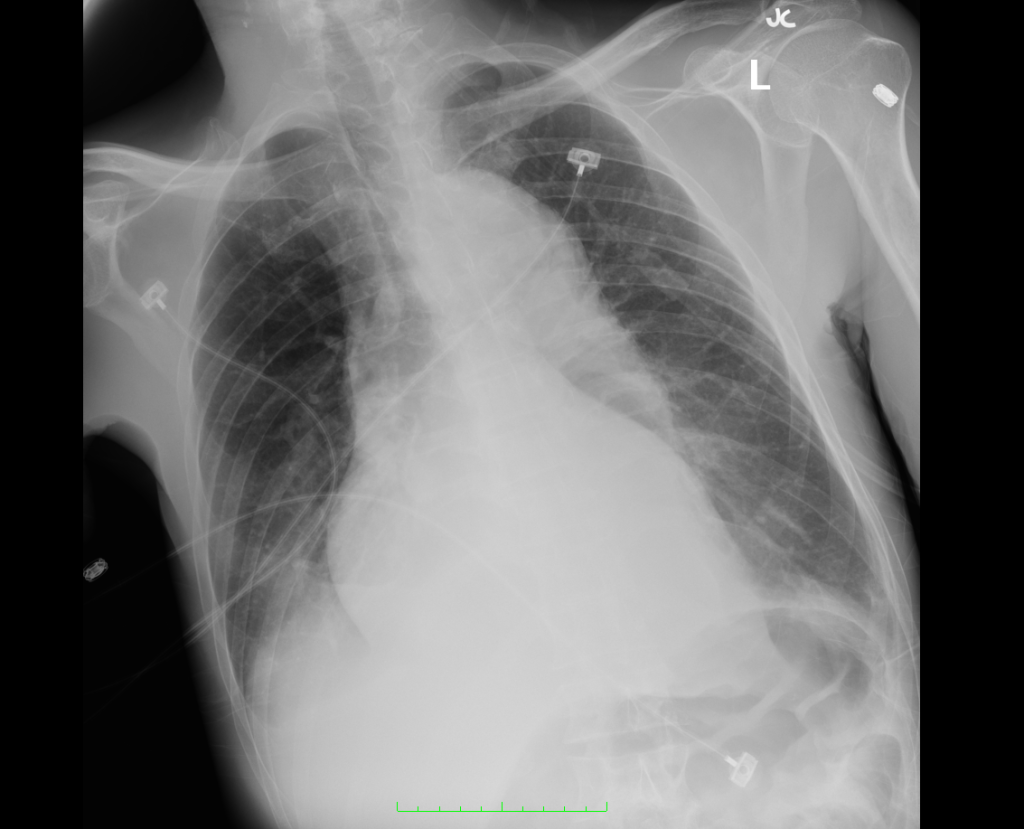
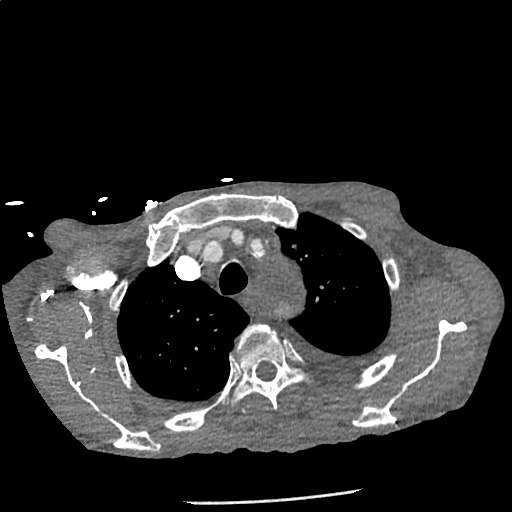
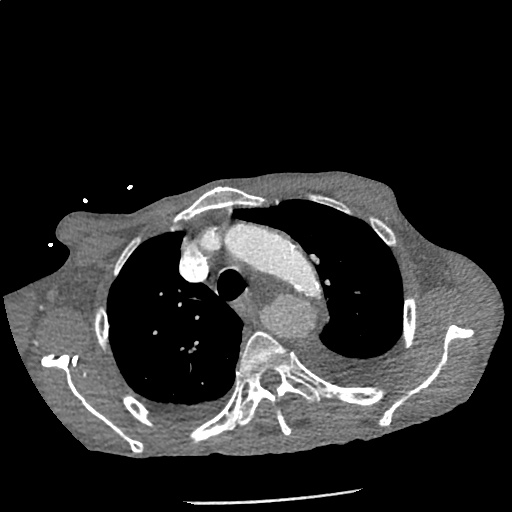
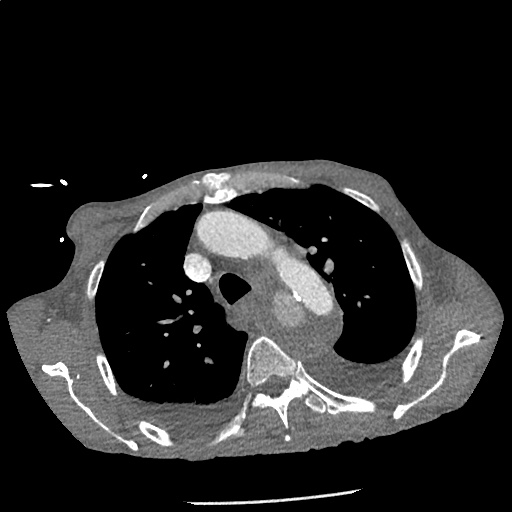
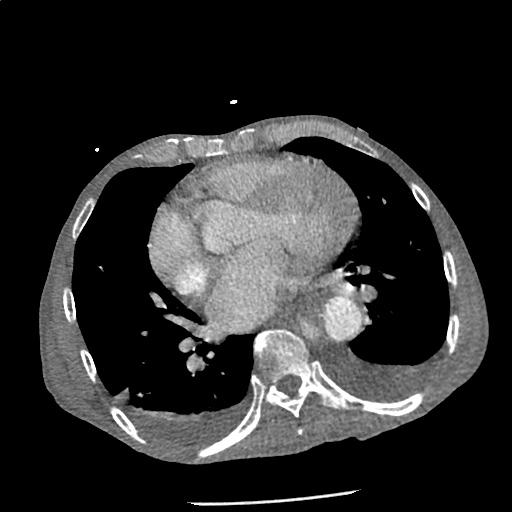
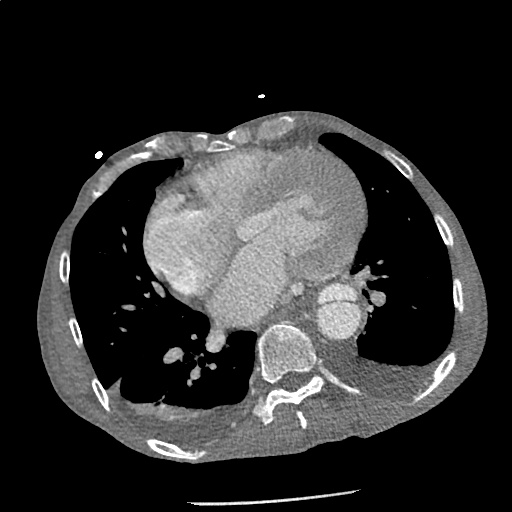
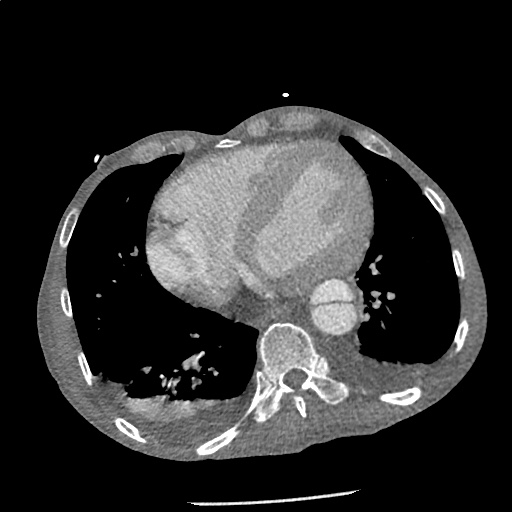
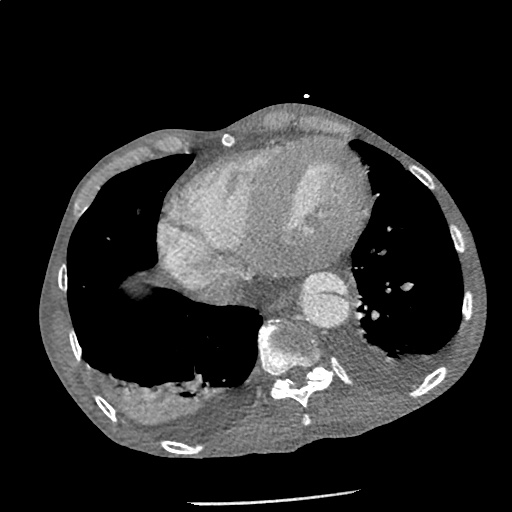
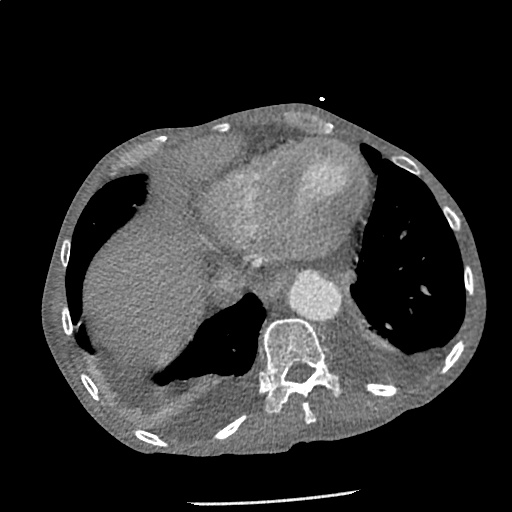
CT Angiography Aorta
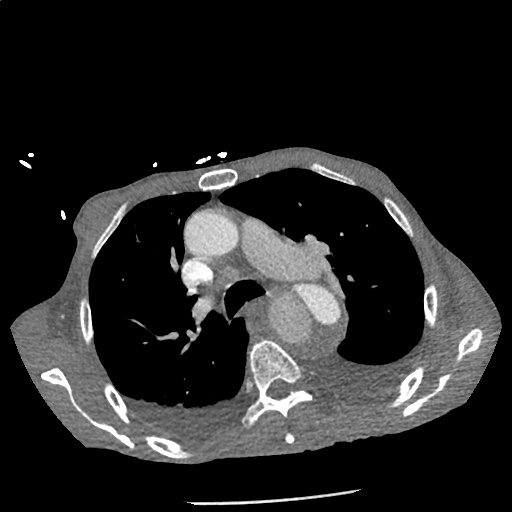
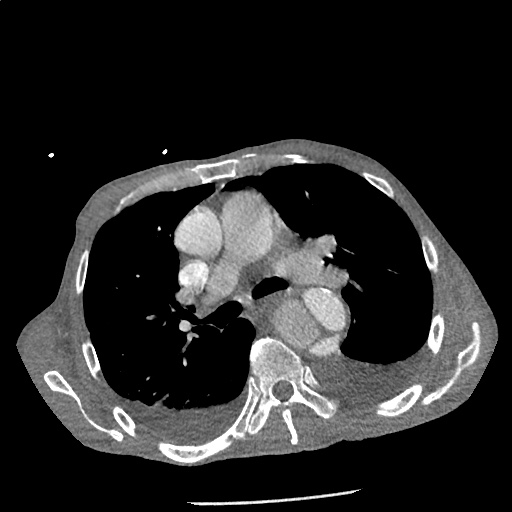
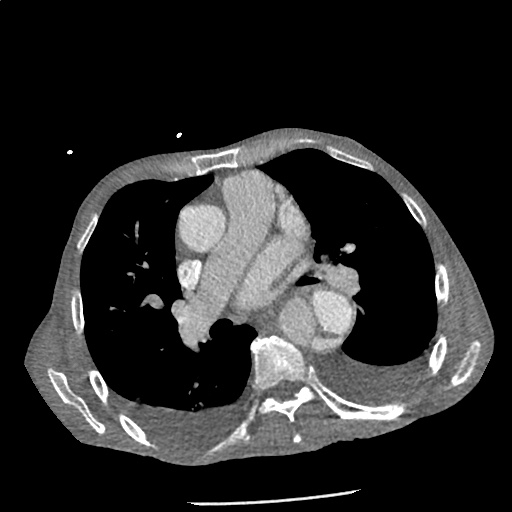
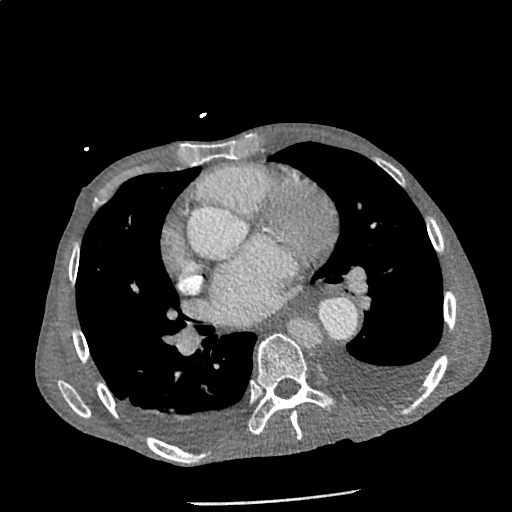
Highly complex type B aortic dissection originating at the distal arch (just distal to the left subclavian artery) and terminating at the level of diaphragm. The dissection contains multiple false lumens containing blood products of differing ages (thrombus and contrast-opacified blood). No apparent involvement of the left common carotid or left subclavian artery.
Mediastinum Anatomy
Mediastinal Masses
- Anterior
- Retrosternal goiter
- Thymoma
- Germ-cell tumor
- Lymphadenopathy (lymphoma)
- Middle
- Aortic arch aneurysm
- Dilated pulmonary artery
- Tracheal lesion
- Posterior
- Esophageal lesions
- Hiatal hernia
- Descending aortic aneurysm
- Paraspinal abscess
- Faiz, O., & Moffat, D. (2002). Anatomy at a glance. Malden, MA: Blackwell Science.
- Whitten CR, Khan S, Munneke GJ, Grubnic S. A diagnostic approach to mediastinal abnormalities. Radiographics. 2007;27(3):657–671. doi:10.1148/rg.273065136.
- WikEM: Widened mediastinum