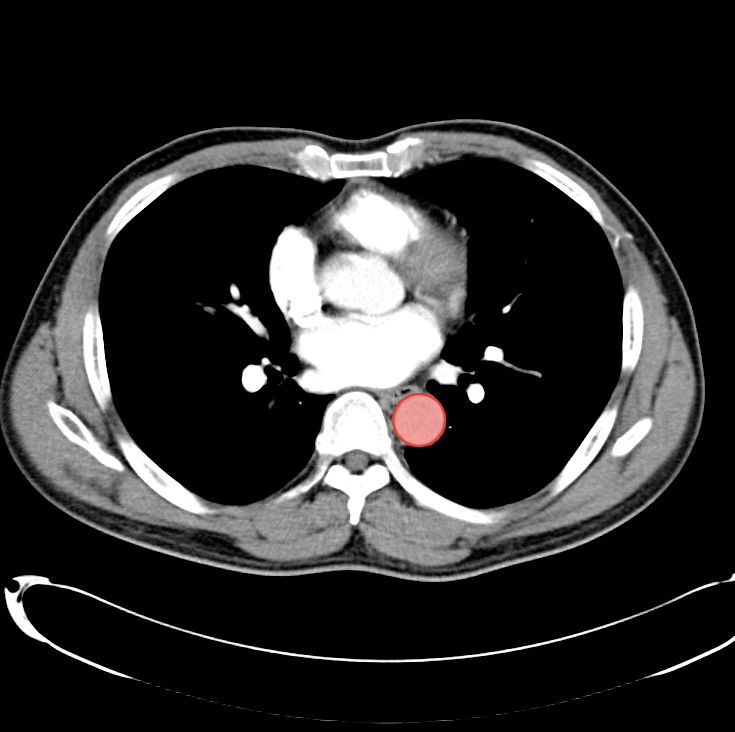
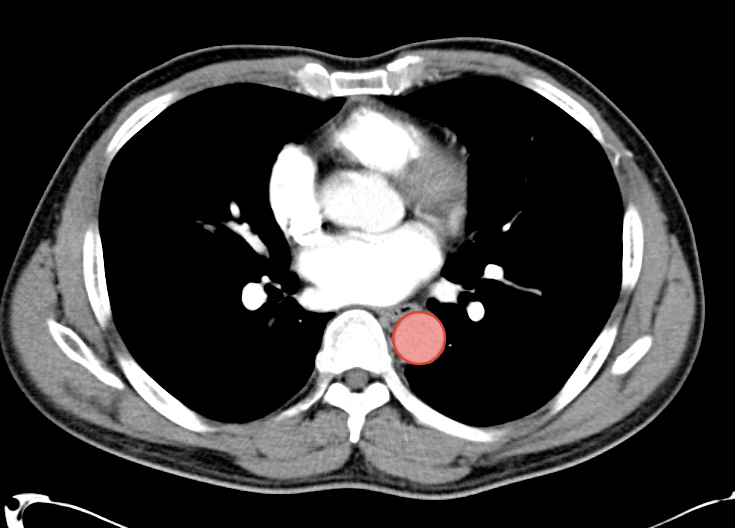
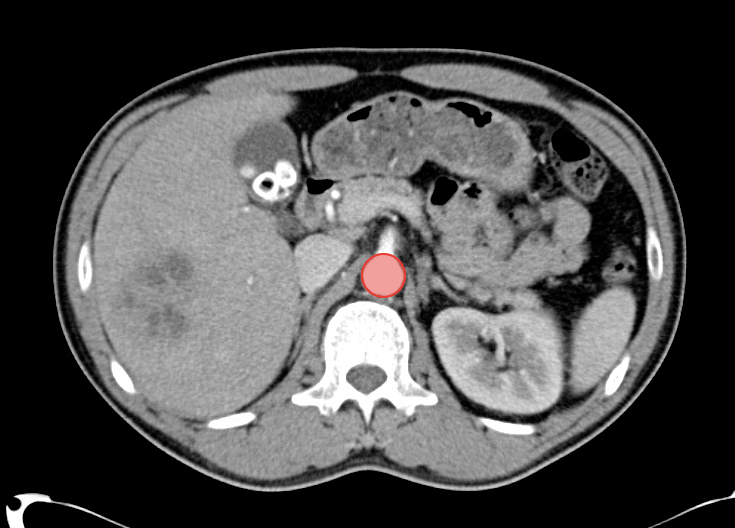
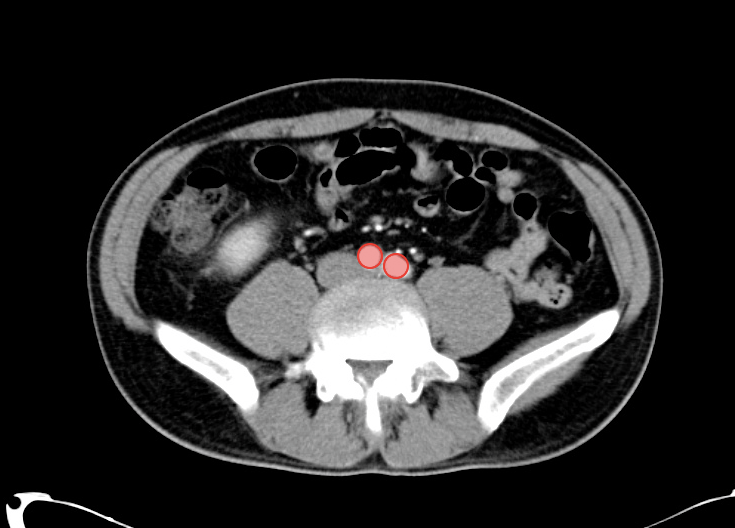
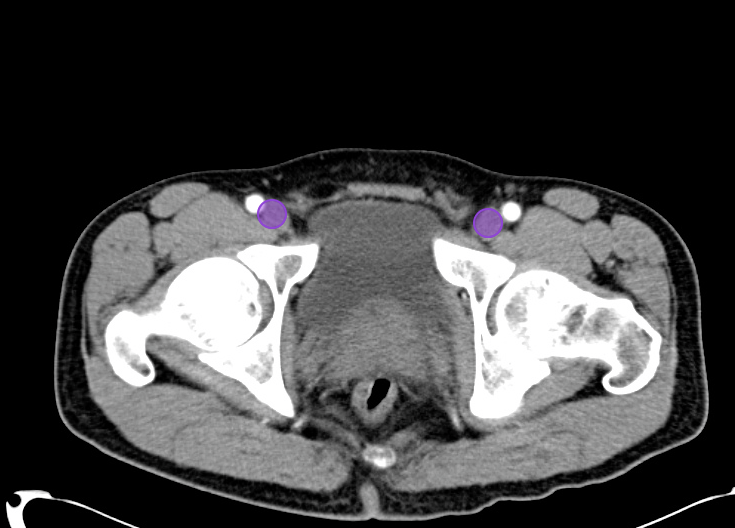
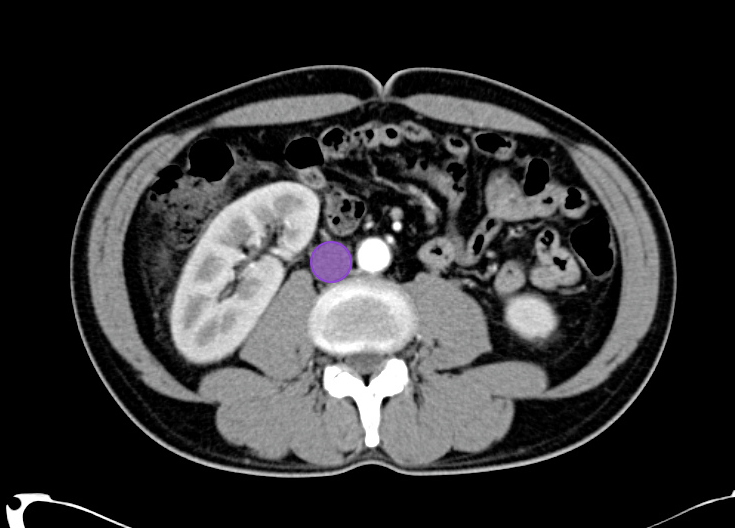
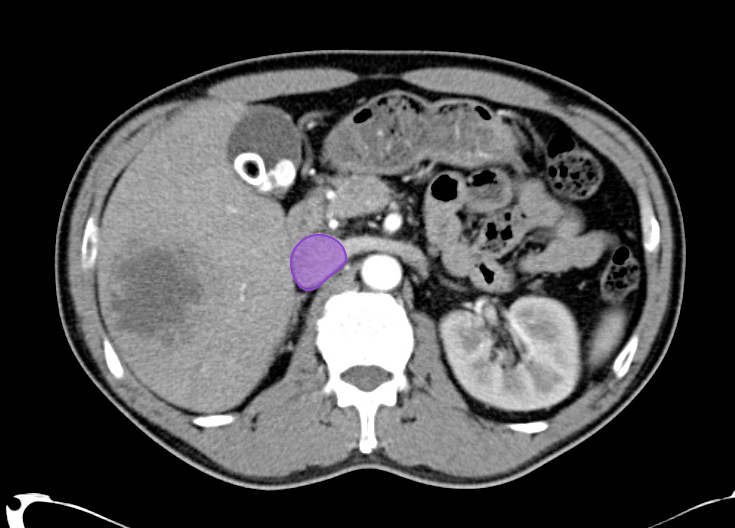
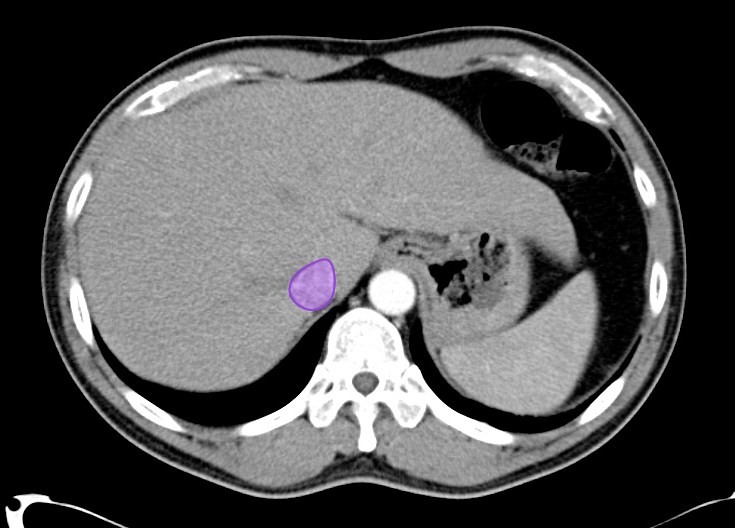
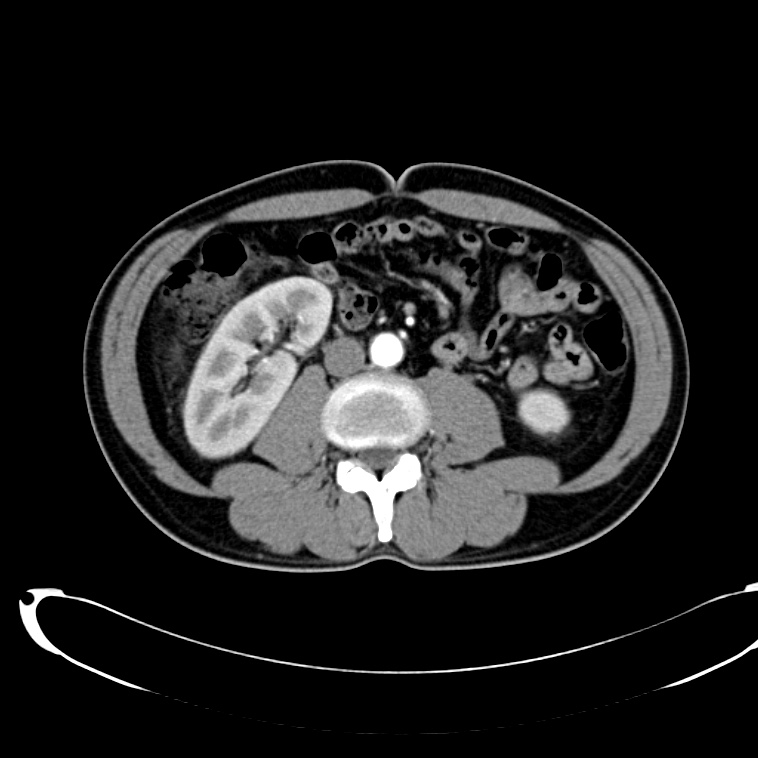
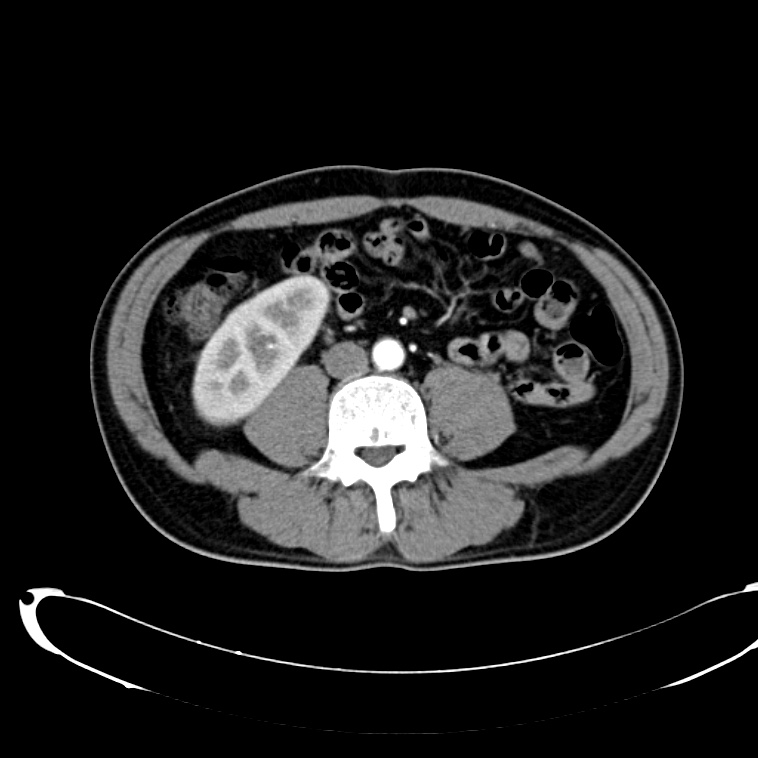
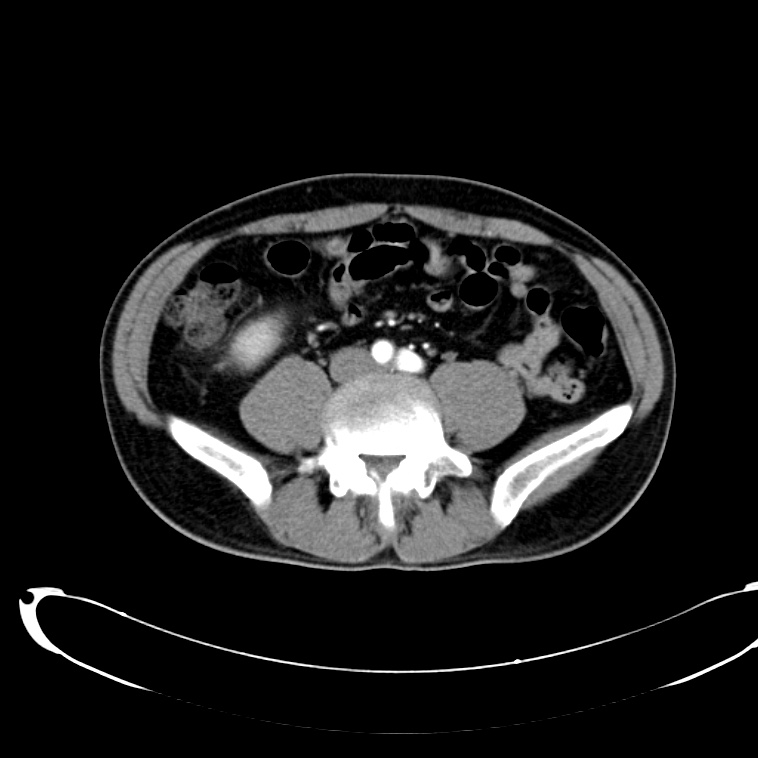
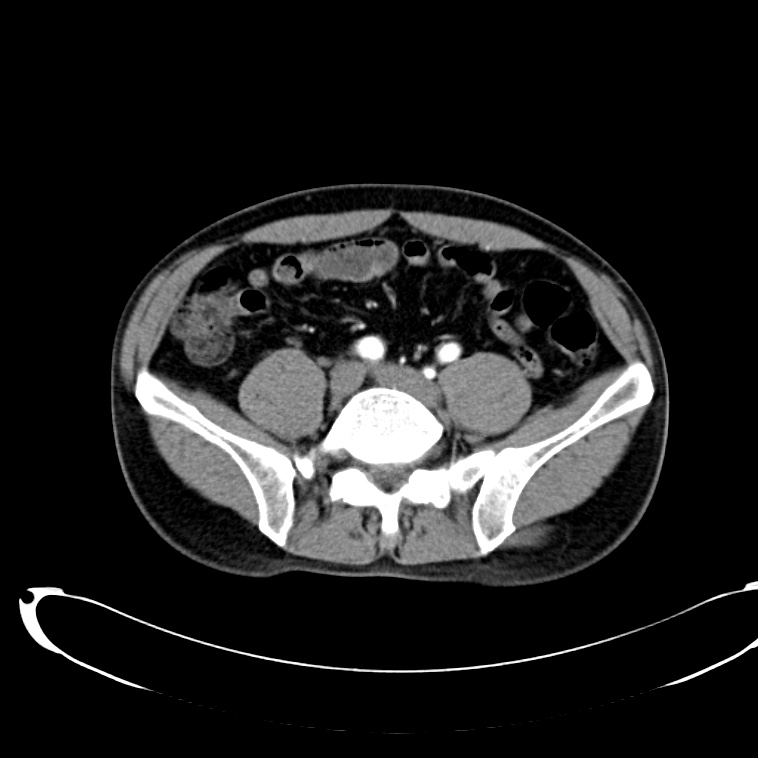
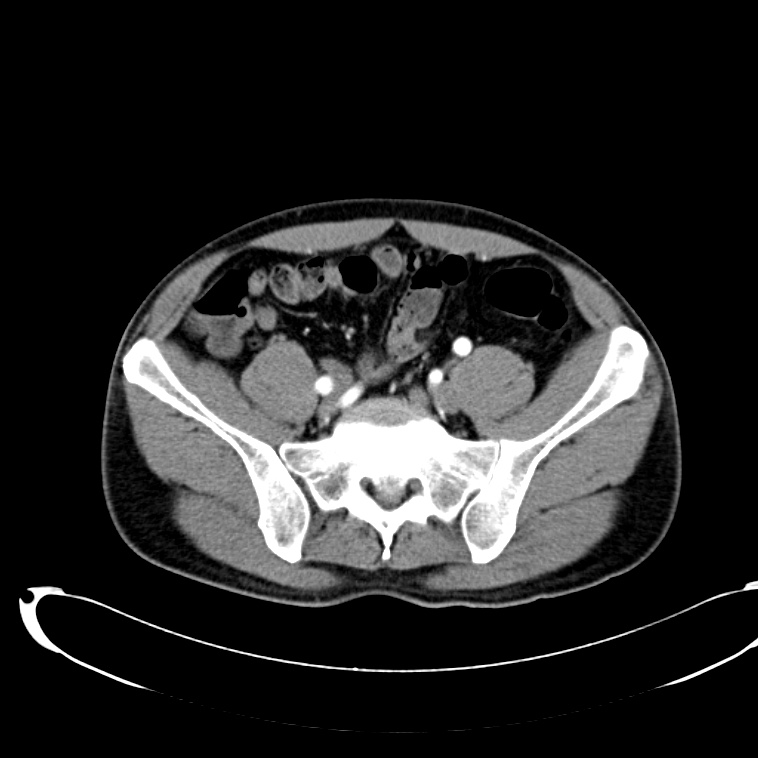
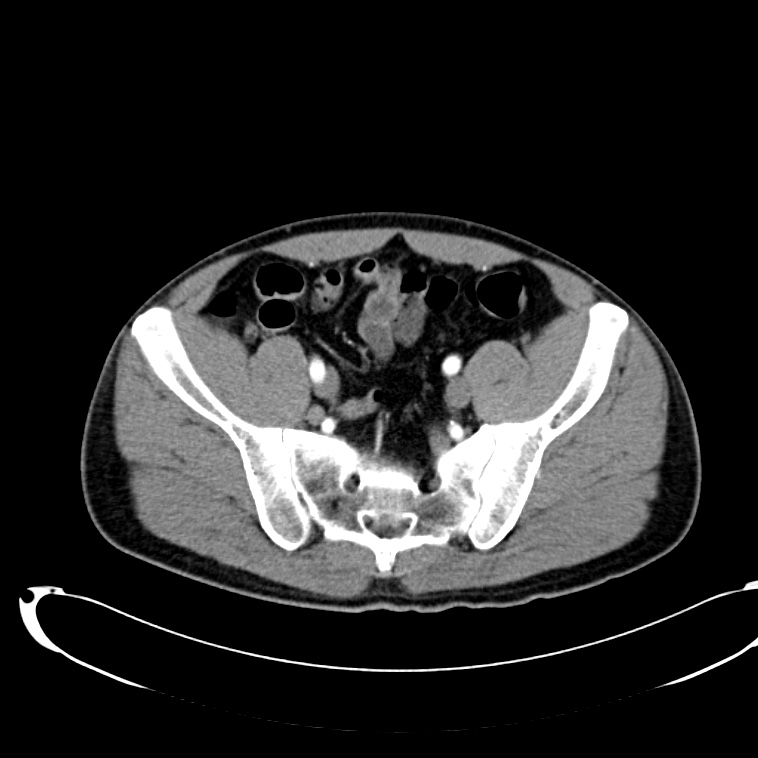
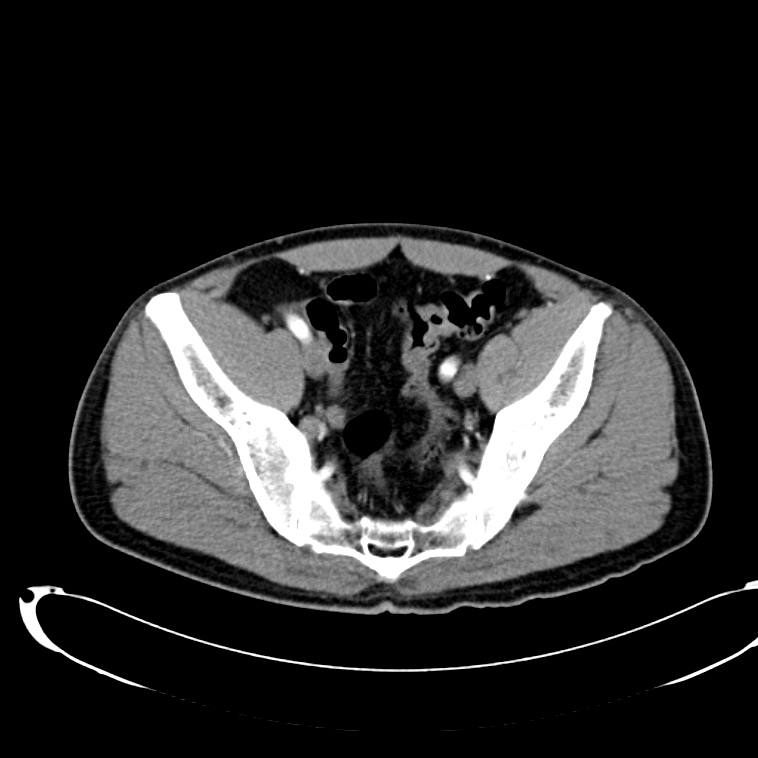
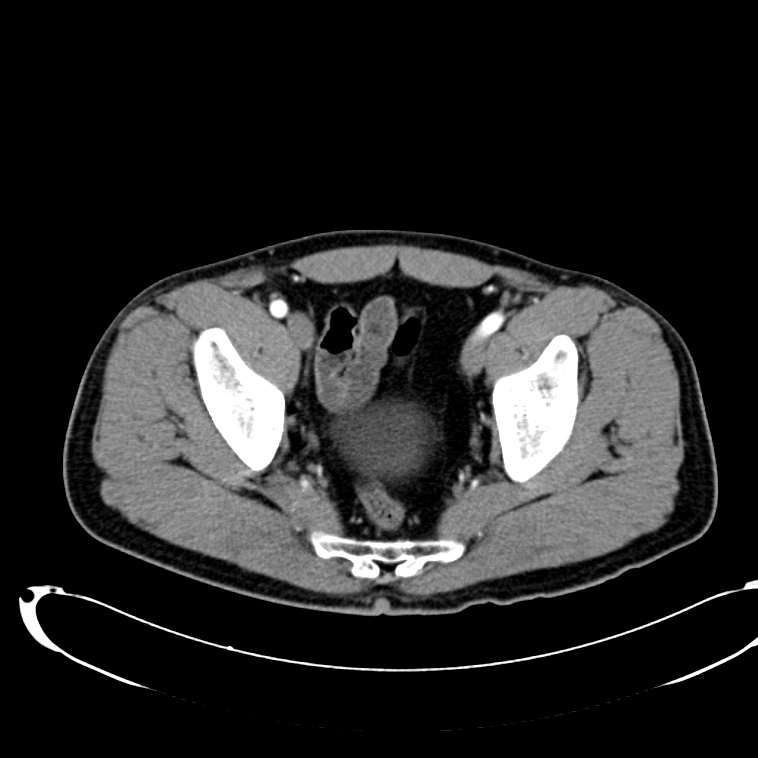
As with the systematic approach preferred for the evaluation and management of other processes explored on this site, a similarly structured method for the interpretation of imaging commonly obtained in the emergency department may afford the same benefits – namely, the timely identification of pathology while avoiding costly missed diagnoses. In this post, I propose an approach to the interpretation of computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis.
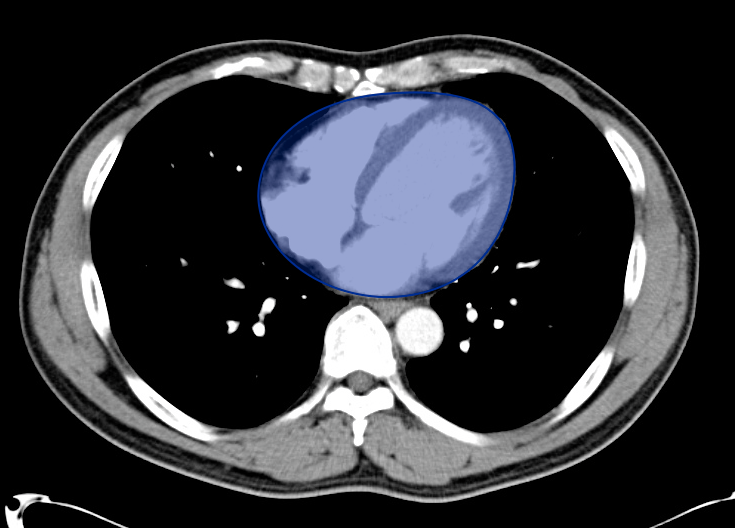
Aorta Down
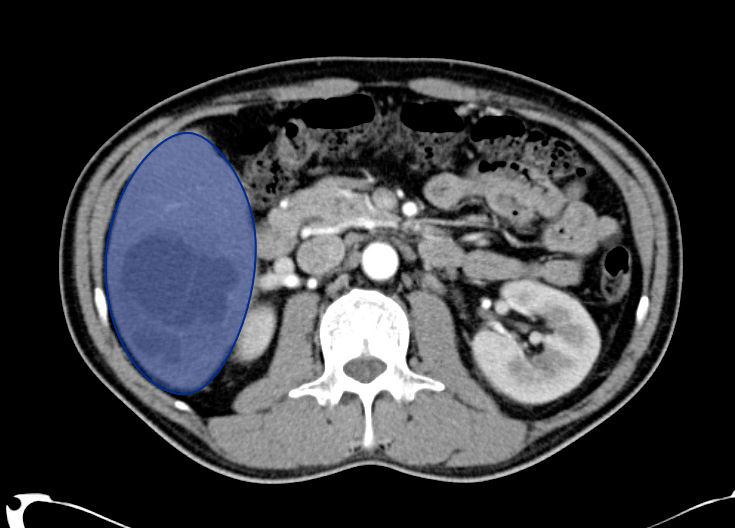
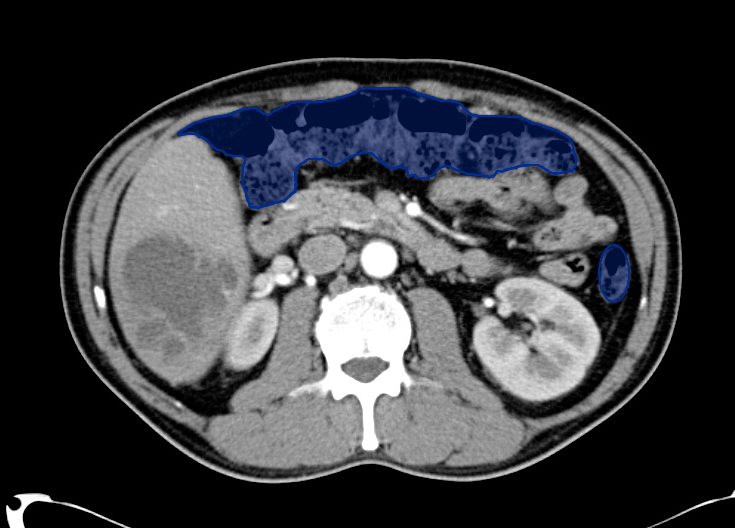
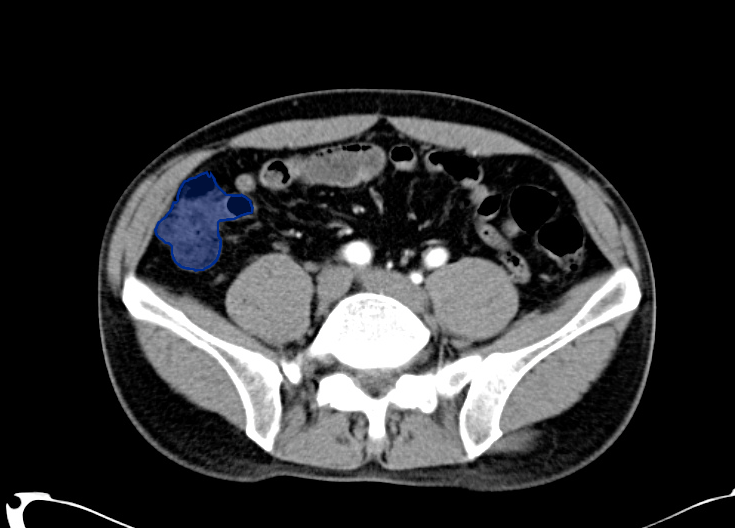
Veins Up
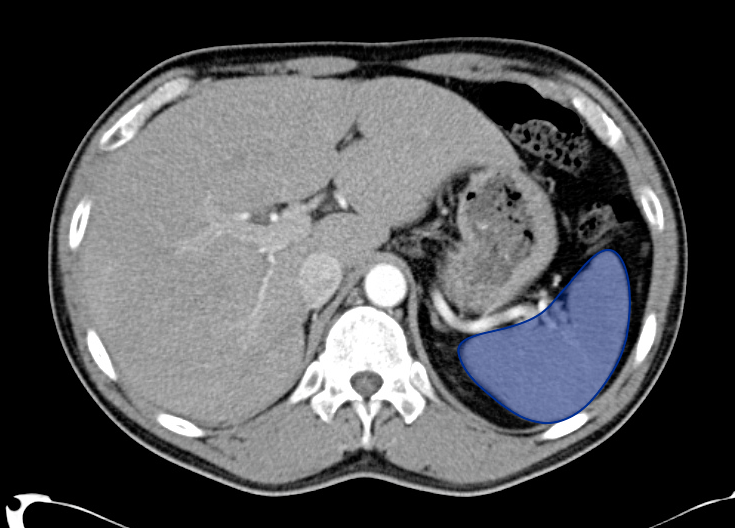
Solid Organs Down
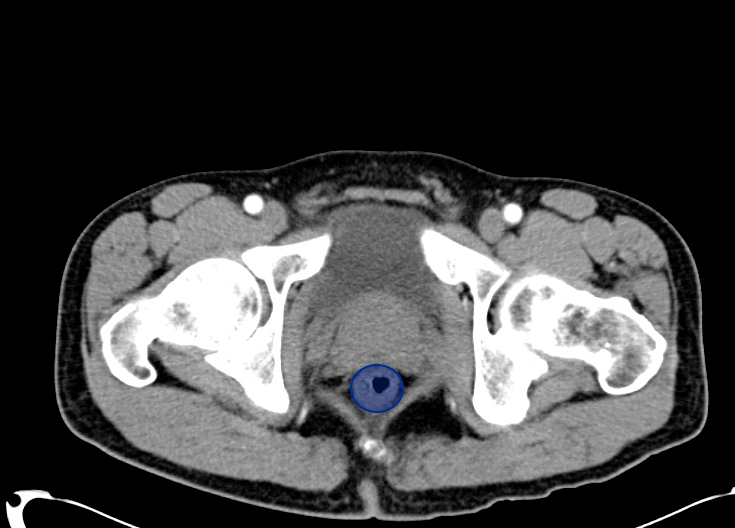
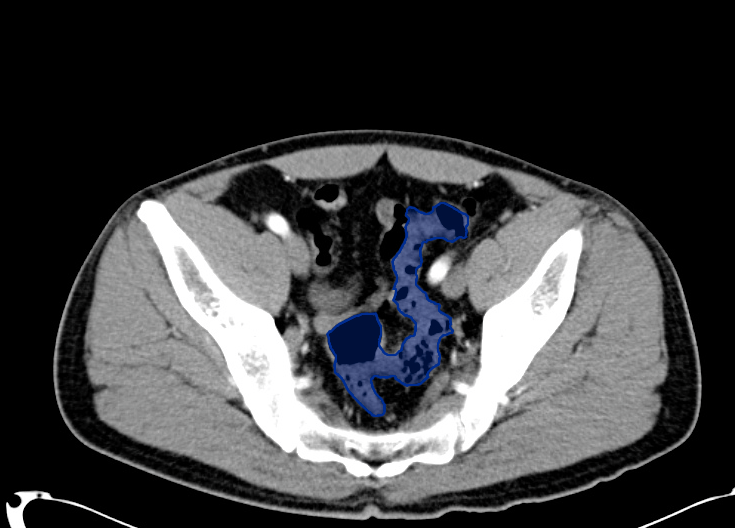
Rectum Up
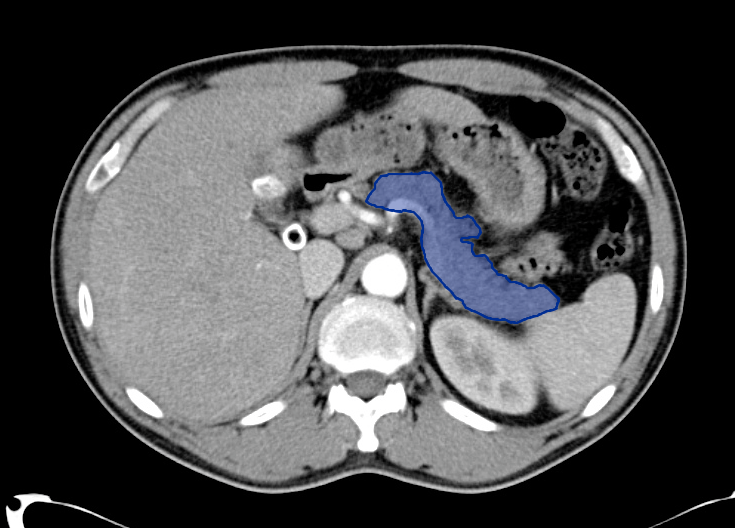
Esophagus Down
Tissue-specific Windows
Try It Yourself
CT Abdomen/Pelvis Interpretation
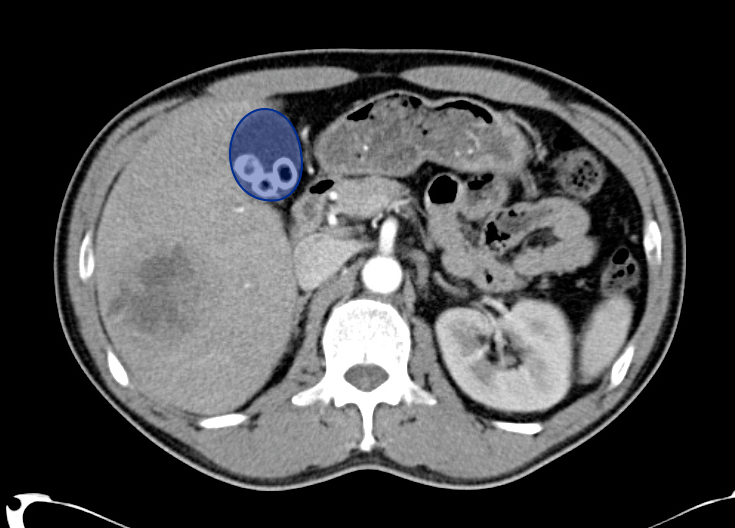
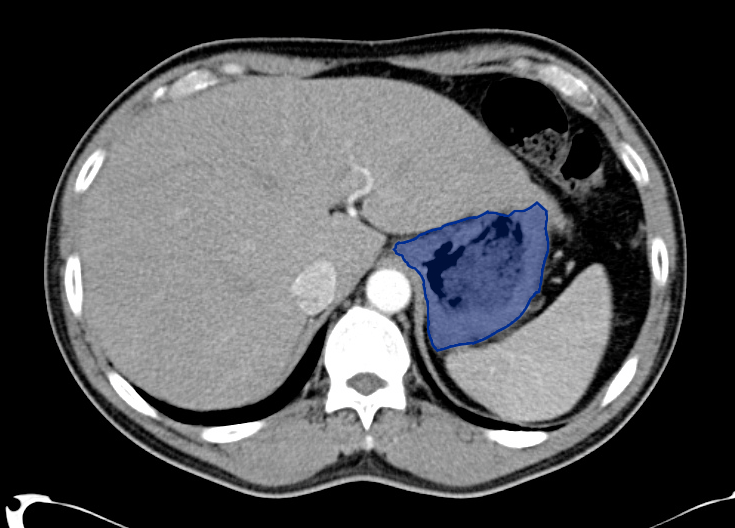
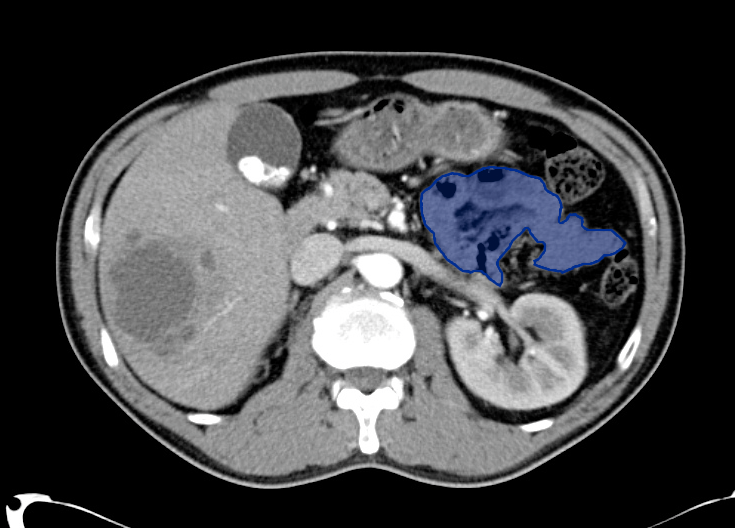
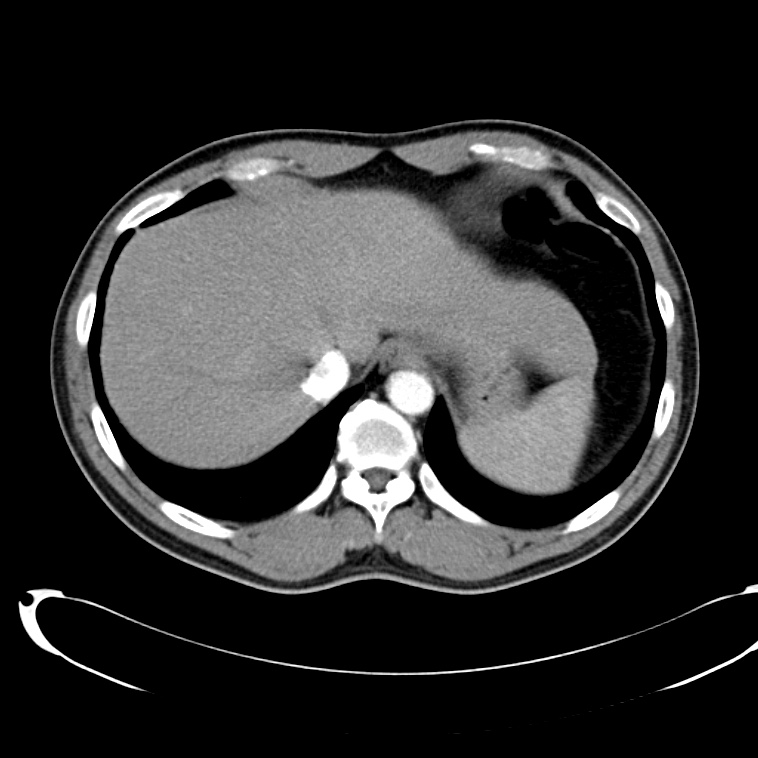
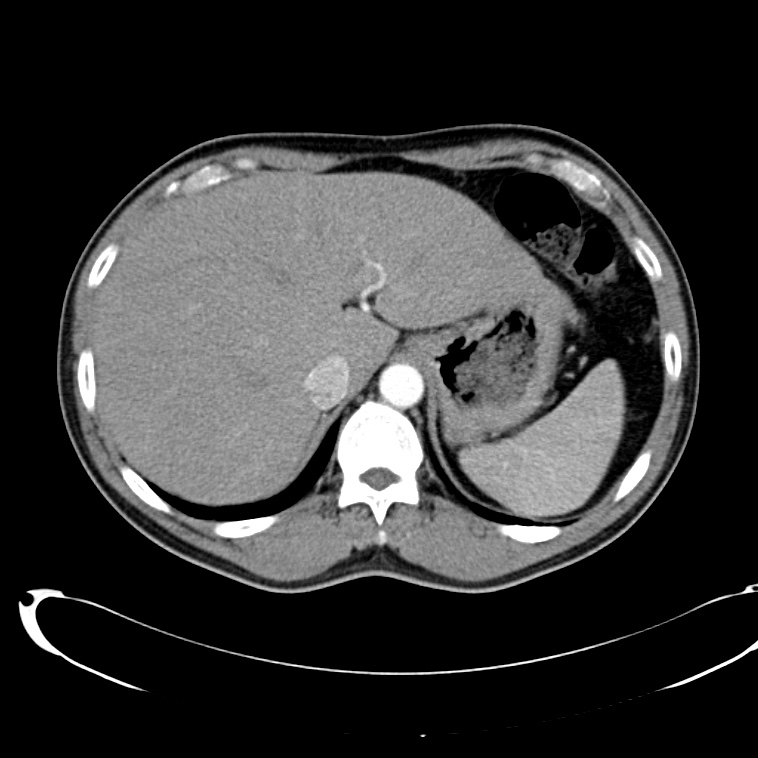
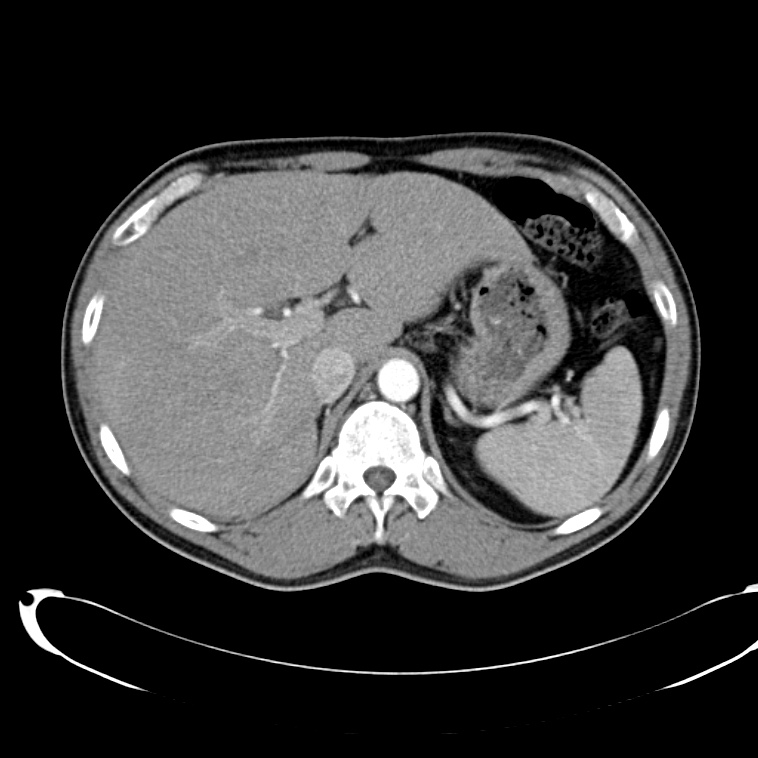
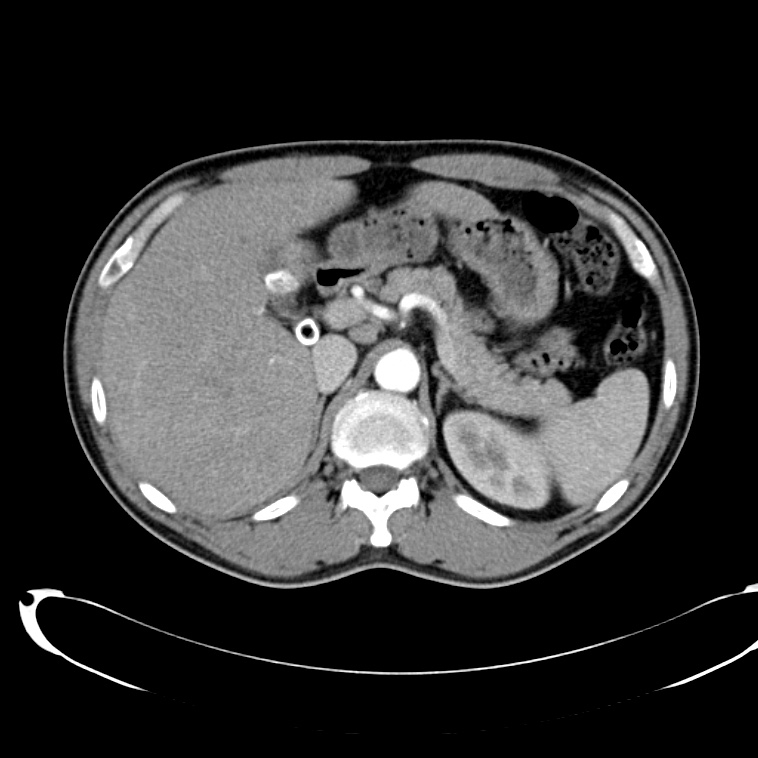
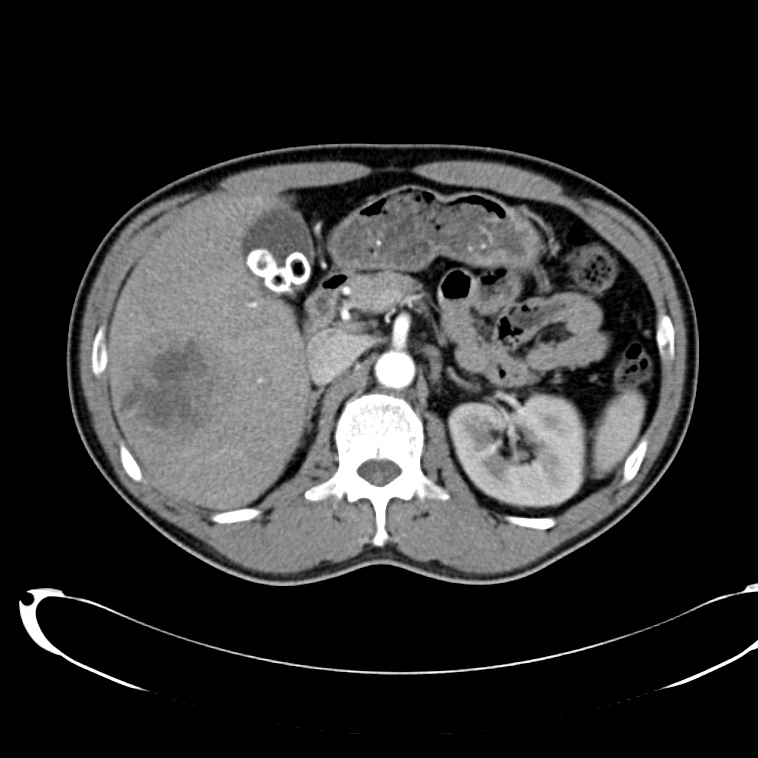
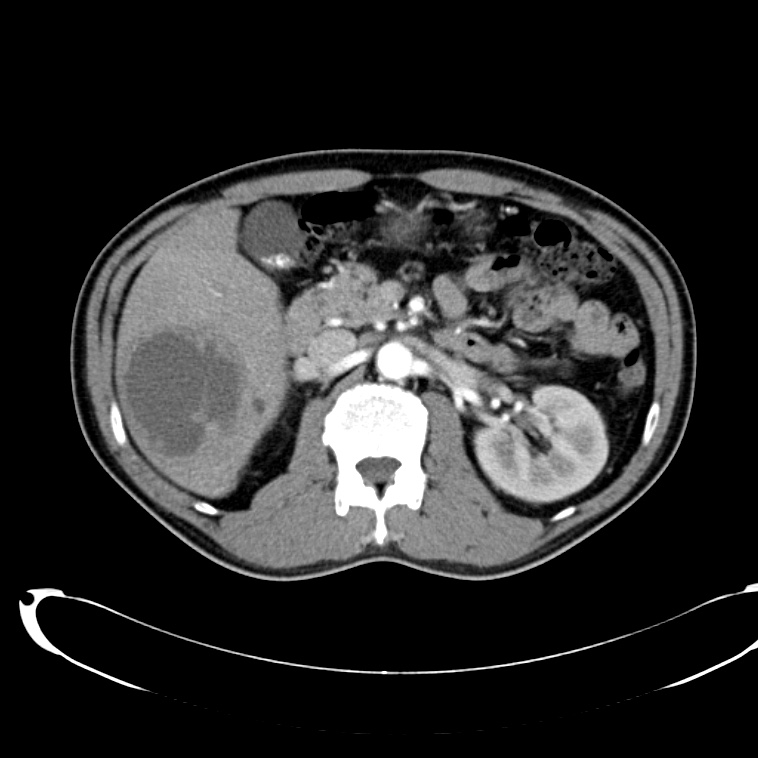
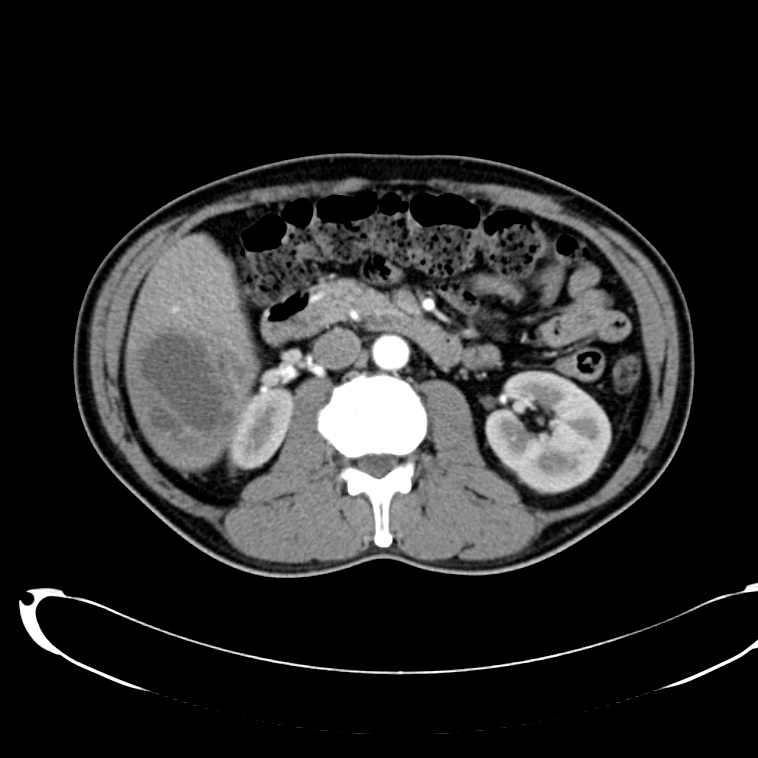
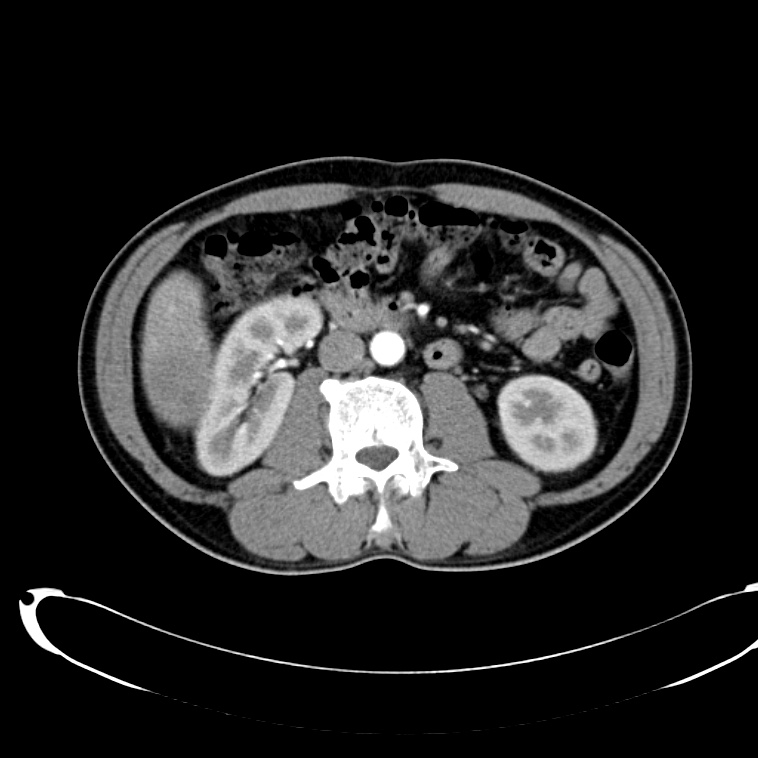
- Cystic lesion in the inferior right lobe of the liver most consistent with hepatic abscess.
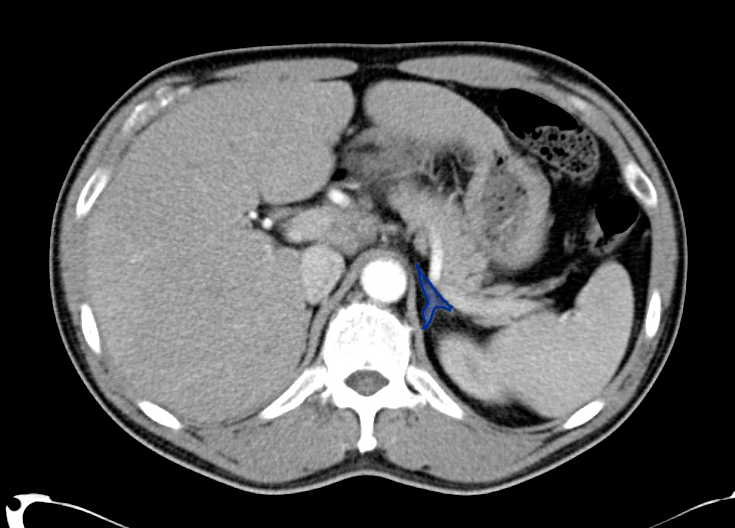
- Multiple calcified gallstones in the gallbladder.