ECG Standard
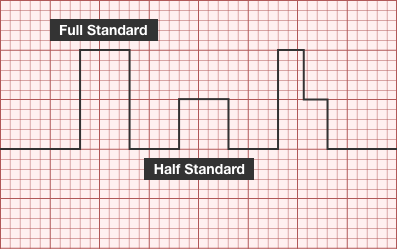
- Full standard: no adjustment
- Half-standard: commensurate reduction in amplitude (usually 50%)
- Mixed: reduction in amplitude of precordial leads
Atrial Abnormalities
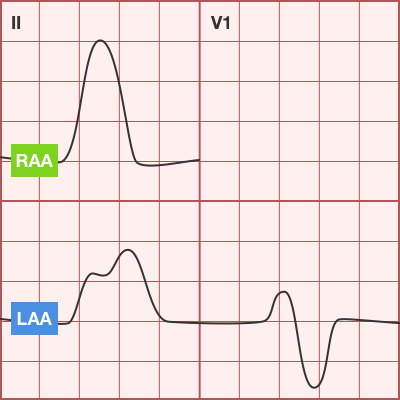
- Right Atrial Abnormality (P pulmonale)
- Peaked P-wave in II (>3mm from 0-6mo or >2.5mm >6mo)
- Causes: right atrial volume overload, ASD, Ebstein, Fontan
- Left Atrial Abnormality (P mitrale)
- Wide, notched P-wave in II or biphasic in V1
- Causes: MS, MR
Axis
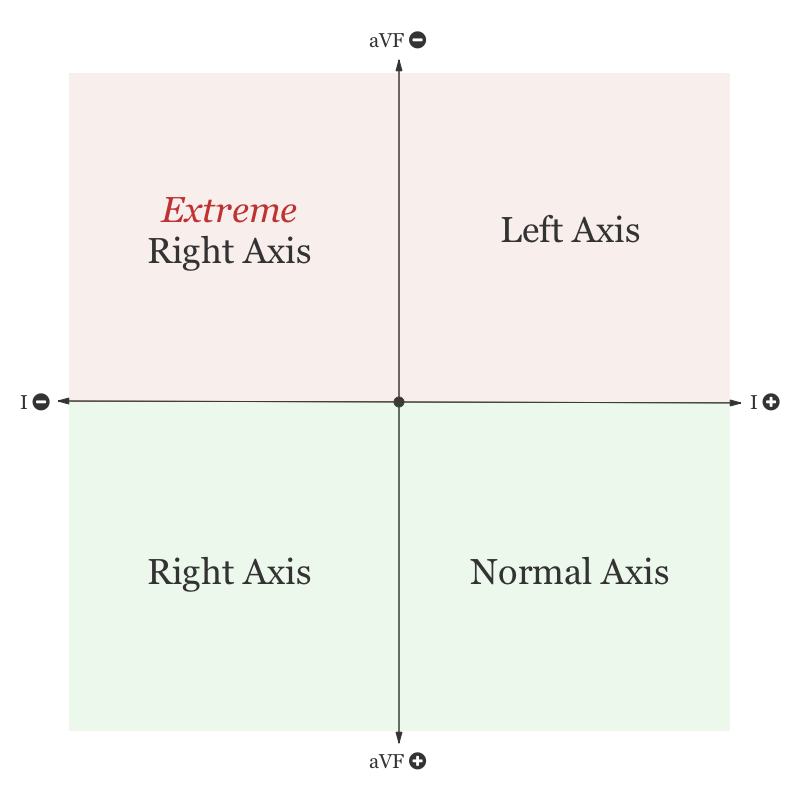
- Anatomical dominance of right ventricle until approximately 6mo
- RAD normal
- eRAD suggests AV canal defect
T-waves
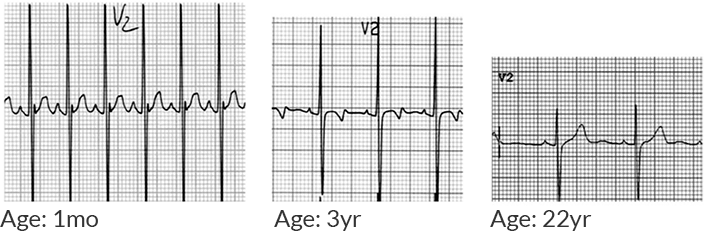
- 1st week of life: Upright
- Adolescent: Inverted
- Adult: Upright
Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
- R-wave height >98% for age in lead V1
- S-wave depth >98% for age in lead V6
- T-wave abnormality (ex. upright in childhood)
- Causes: pHTN, PS, ToF
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- R-wave height >98% for age in lead V6
- S-wave depth >98% for age in lead V1
- Adult-pattern R-wave progression in newborn (no large R-waves and small S-waves in right precordial leads)
- Left-axis deviation
- Causes: AS, coarctation, VSD, PDA
Examples
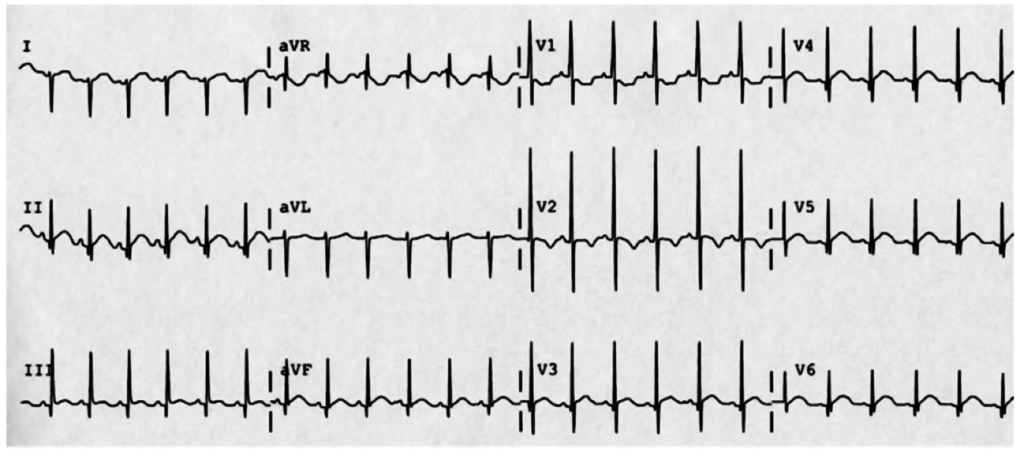
Normal Neonatal ECG
- 2mo old
- RAD
- Inverted T-waves (normal)
- Tall R-waves in V1-V3
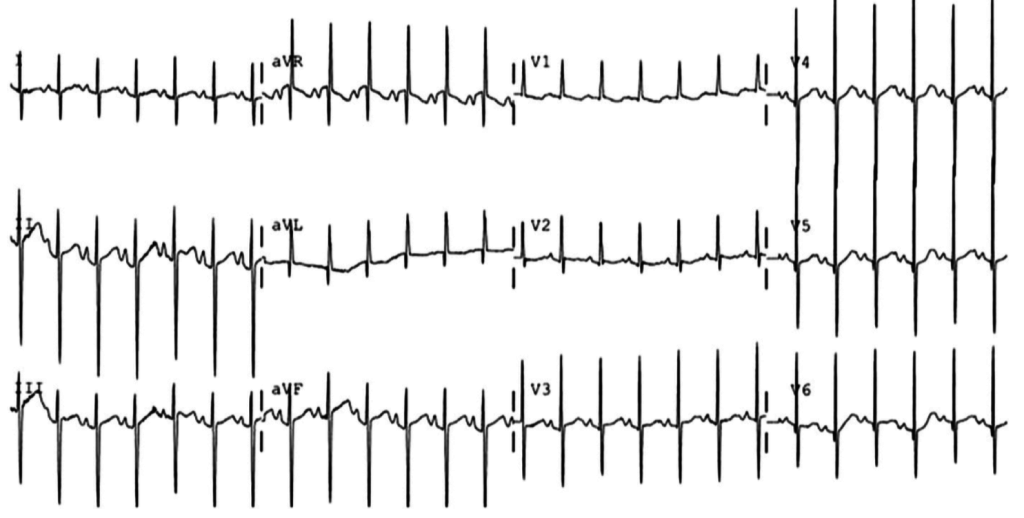
Extreme Axis Deviation
- Neonate with Down syndrome
- Isoelectric in I, Negative in aVF negative in II mean QRS vector -87°
- Extreme RAD suggestive of AV canal defect
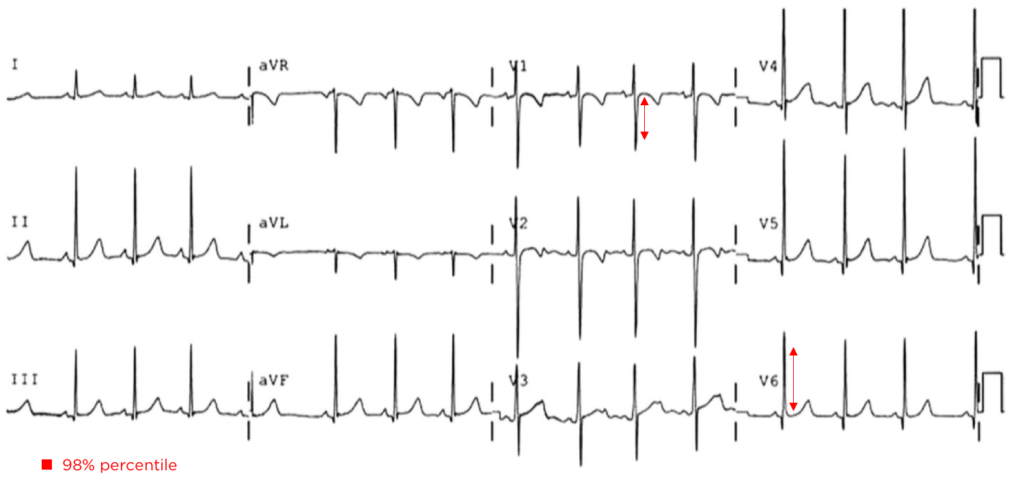
LVH:
- Unrepaired Coarctation
- Deep S-wave in V1 (>98%)
- Tall R-wave in V6 (>98%)
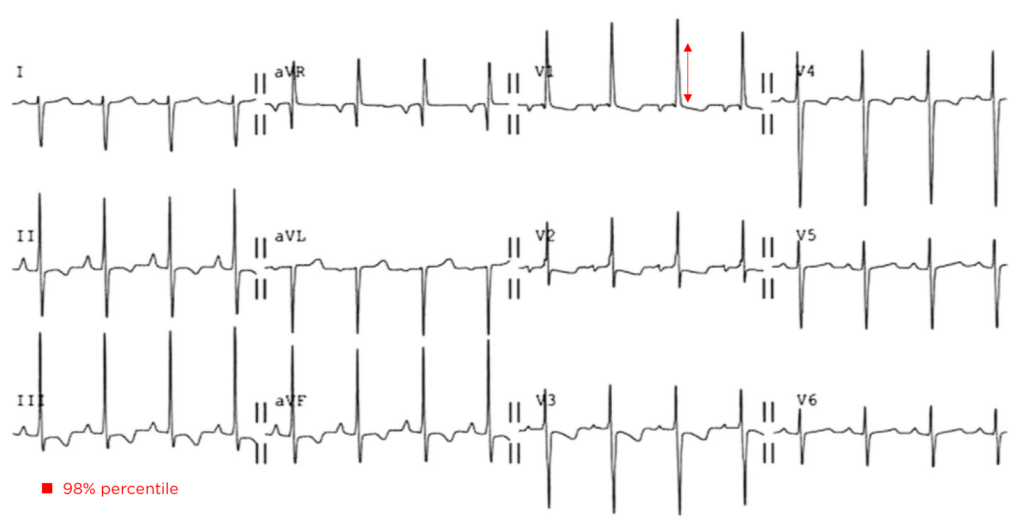
RVH:
- 10 year-old boy with pulmonary Hypertension
- RAD after expected age for normal RAD
- Tall R-waves in V1 (>98%)
- Deep S-wave in V6 (>98%)
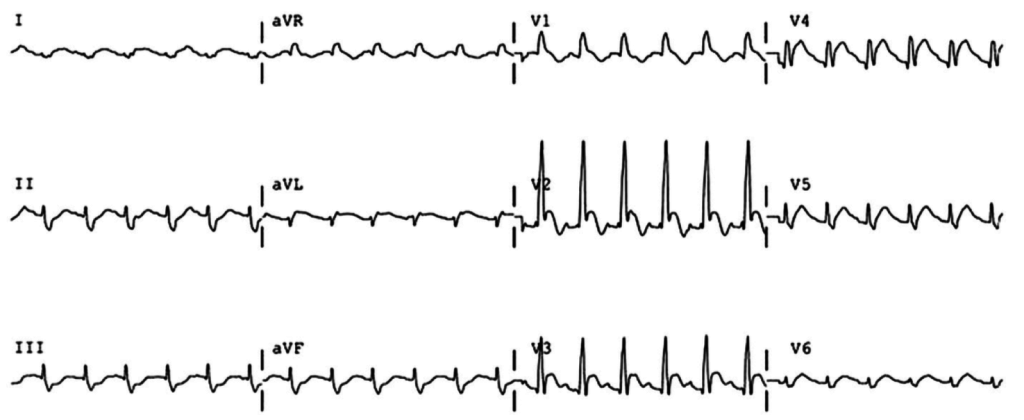
STEMI
- ALCAPA (anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery): coronary artery arises anomalously from the pulmonary artery; as pulmonary arterial pressure falls during the first 6 months of infancy, prograde flow through the left coronary artery ceases and may even reverse.
- HLHS (hypoplastic left heart syndrome): coronary arteries are perfused from a hypoplastic, narrow aorta that is susceptible to flow disruption
- Orthotopic heart transplant with allograft vasculopathy
- Kawasaki: coronary artery aneurysm with subsequent thrombosis
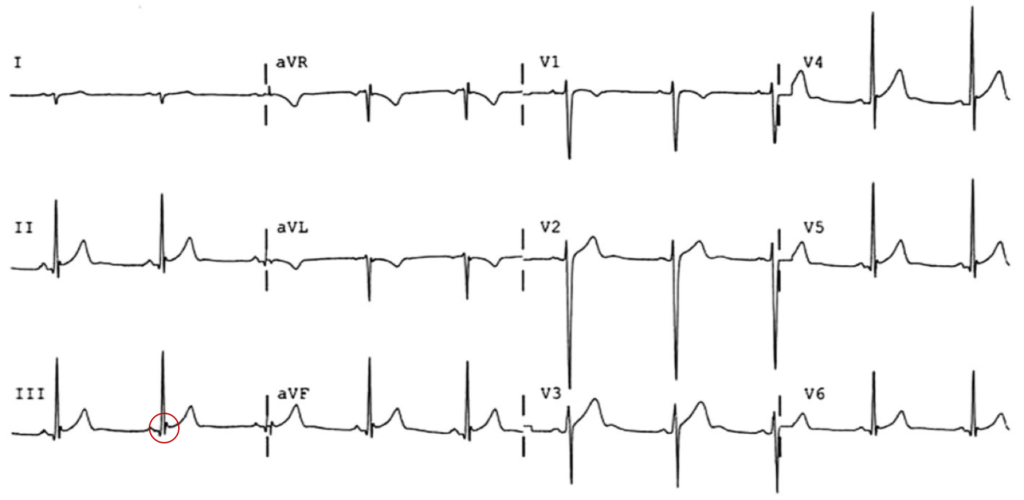
Benign early repolarization
- 14 year-old male
- Concave ST-segment elevation
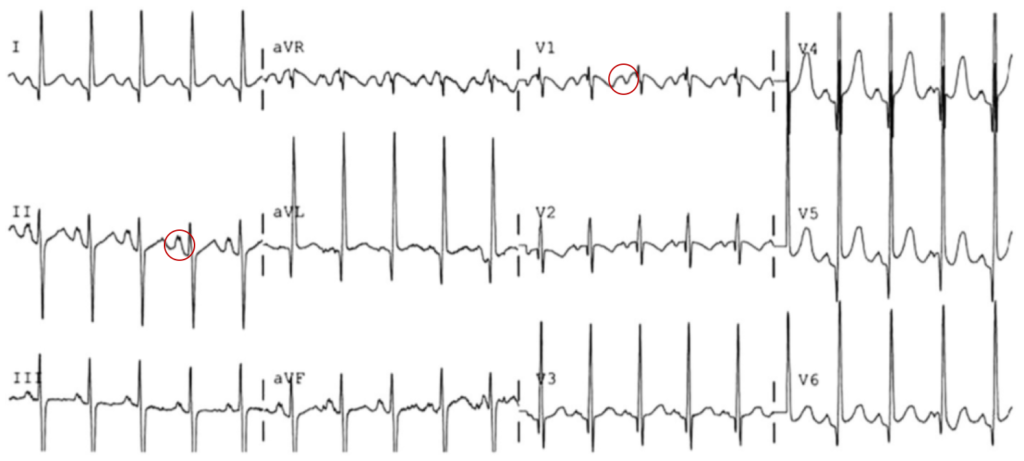
Left Atrial Abnormality:
- 9mo female with mitral insufficiency
- Broad biphasic P-wave in V1
- Tall, notched P-wave in II
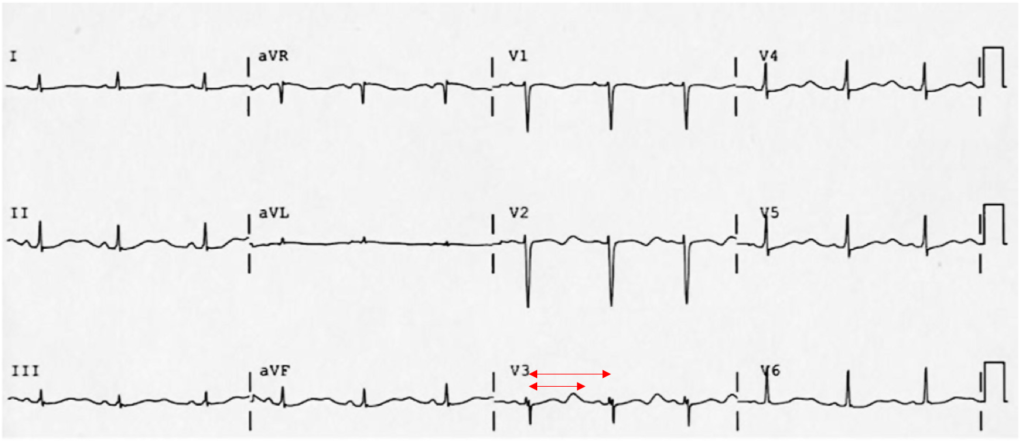
Prolonged QT interval
- 18-year-old female
- Familial long QT syndrome and a history of cardiac arrest
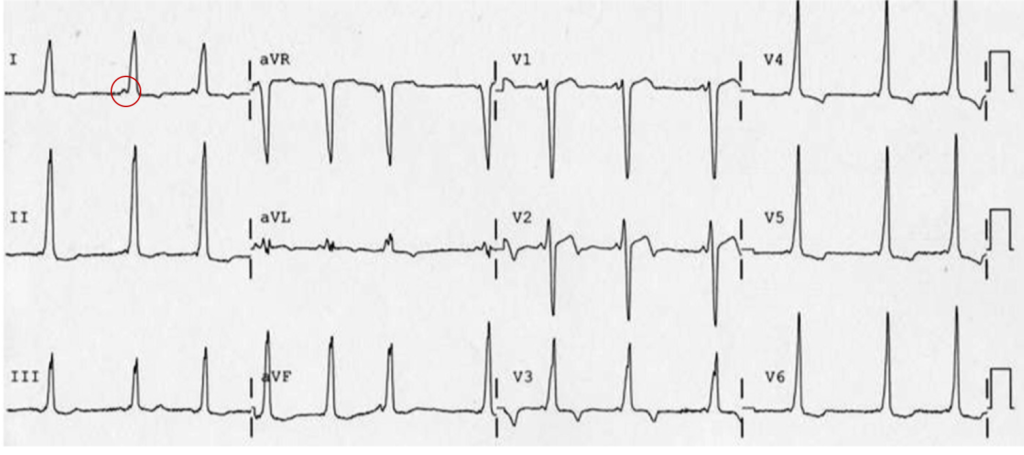
WPW:
- Delta wave, shortened PR interval
References
- O’Connor M, McDaniel N, Brady WJ. The pediatric electrocardiogram. Part I: Age-related interpretation. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(2):221-228. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2007.08.003.
- Goodacre S, McLeod K. ABC of clinical electrocardiography: Paediatric electrocardiography. BMJ. 2002;324(7350):1382-1385.
- O’Connor M, McDaniel N, Brady WJ. The pediatric electrocardiogram Part II: Dysrhythmias. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(3):348-358. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2007.07.034.
- O’Connor M, McDaniel N, Brady WJ. The pediatric electrocardiogram Part III: Congenital heart disease and other cardiac syndromes. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(4):497-503. doi:10.1016/j.ajem.2007.08.004.
- Schwartz P. Guidelines for the interpretation of the neonatal electrocardiogram. Eur Heart J. 2002;23(17):1329-1344. doi:10.1053/euhj.2002.3274.













