Brief HPI:
A 66 year-old male with a history of hypertension and COPD presents with shortness of breath. He states that his symptoms are unimproved with home nebulizer treatments and denies fever, cough or new sputum production. On examination, he has stridor appreciated during inspiratory and expiratory phases.
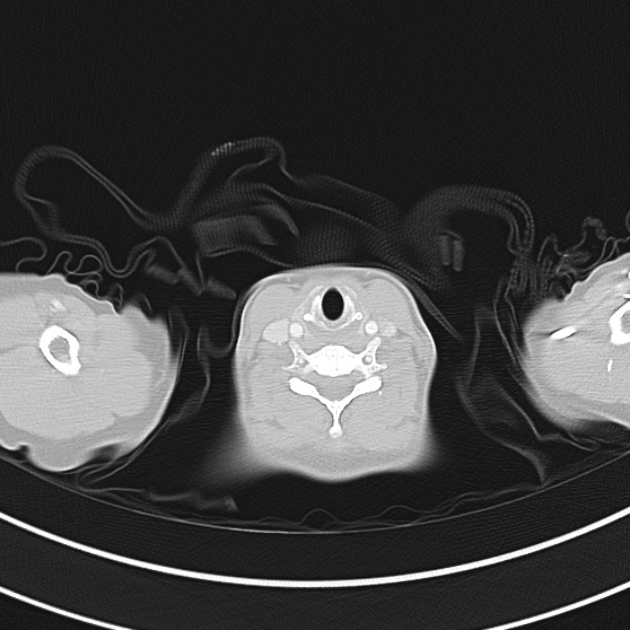
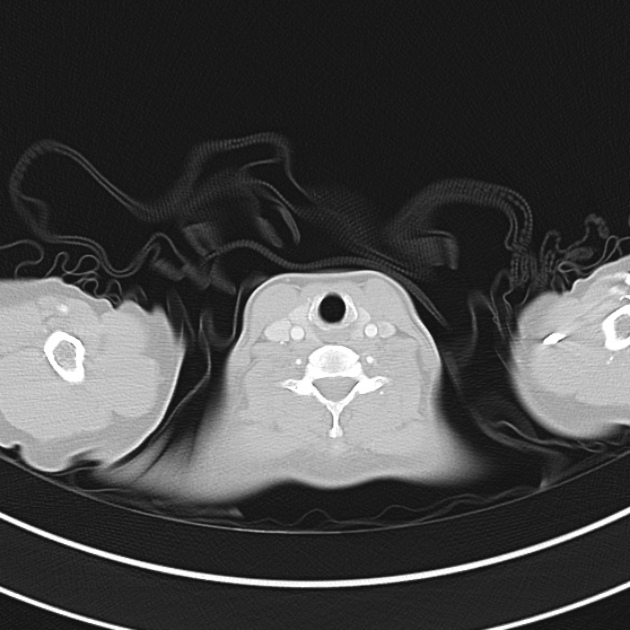
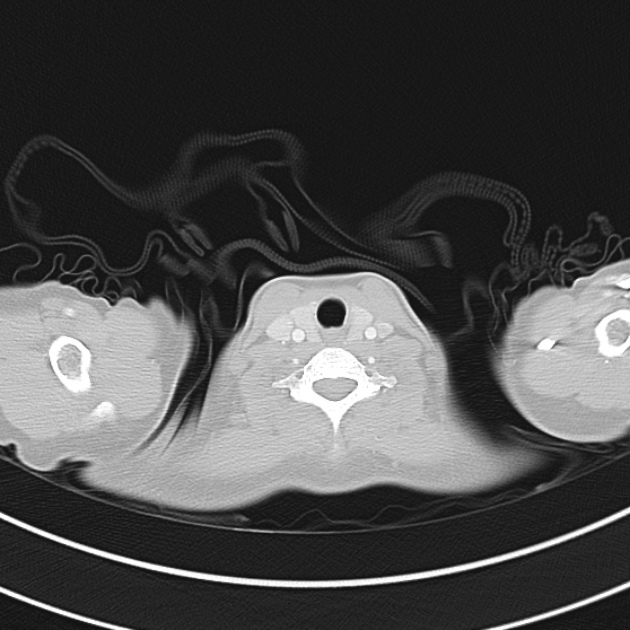
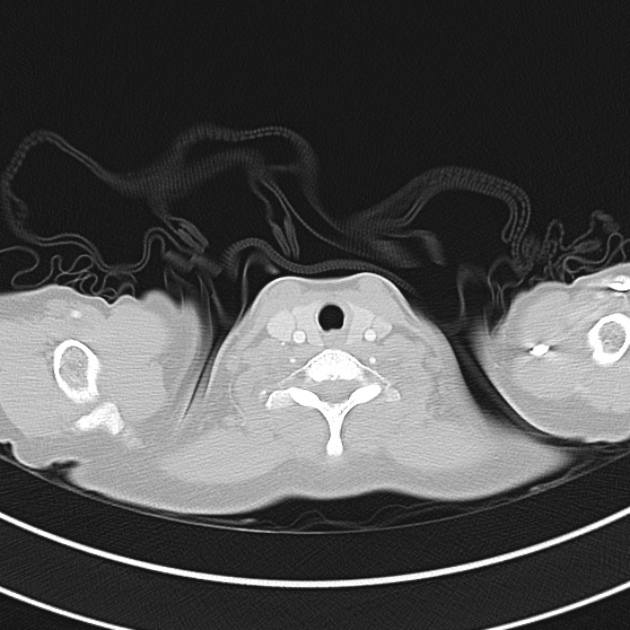
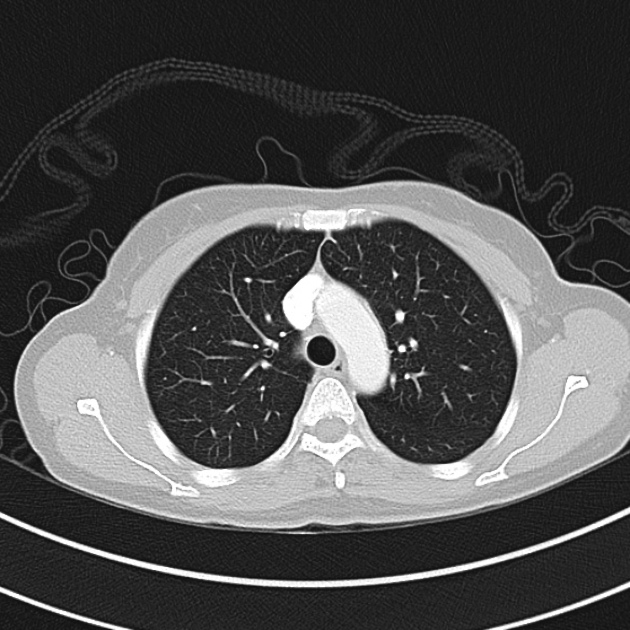
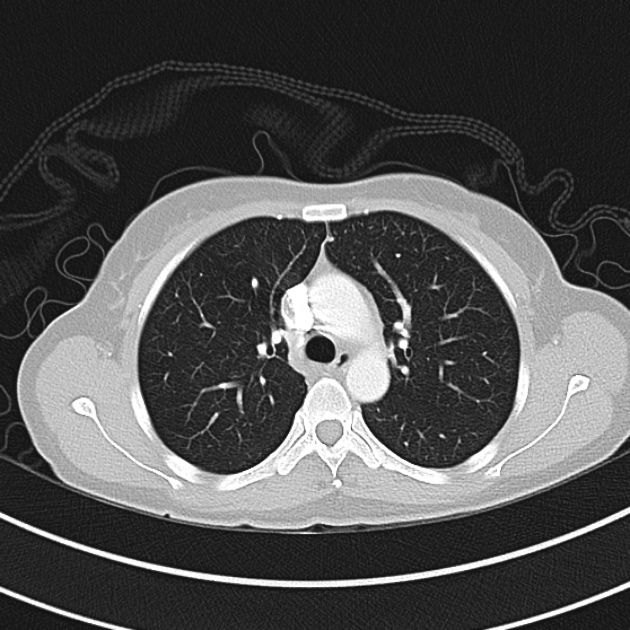
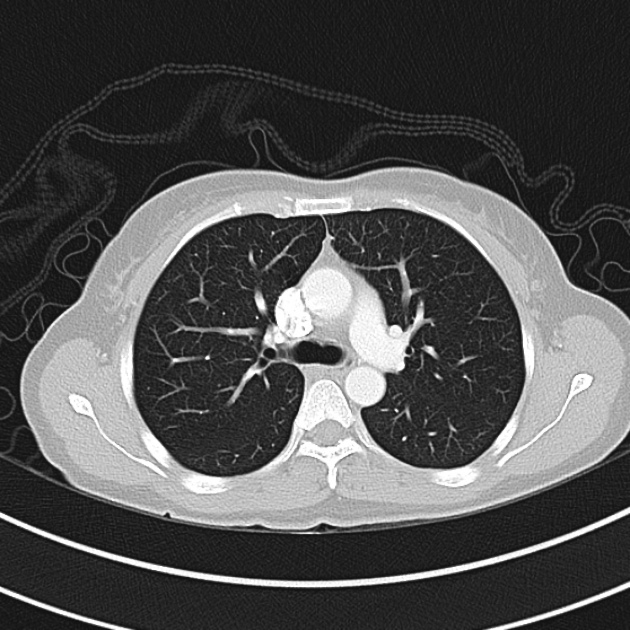
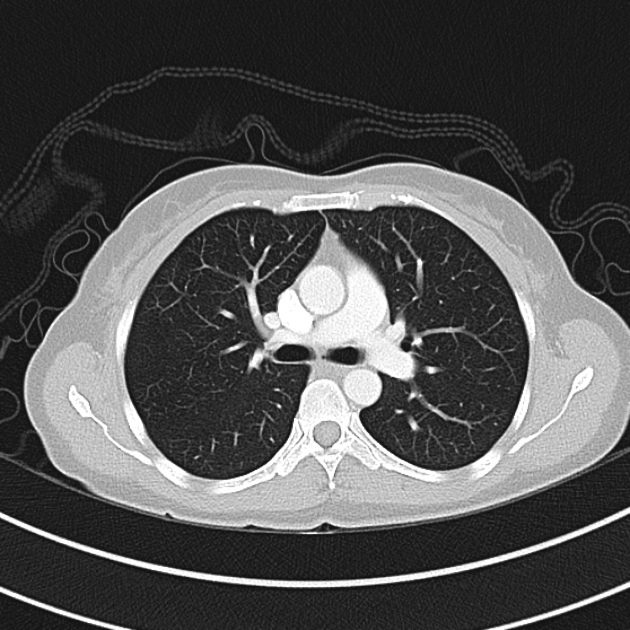
CT Chest:
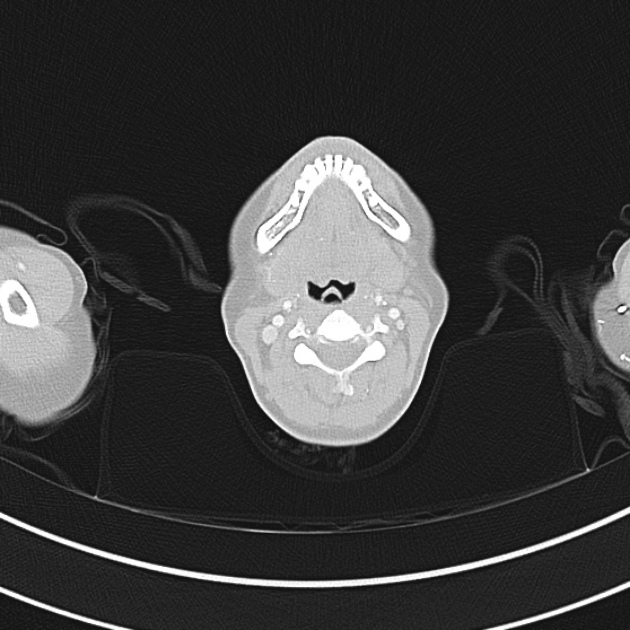
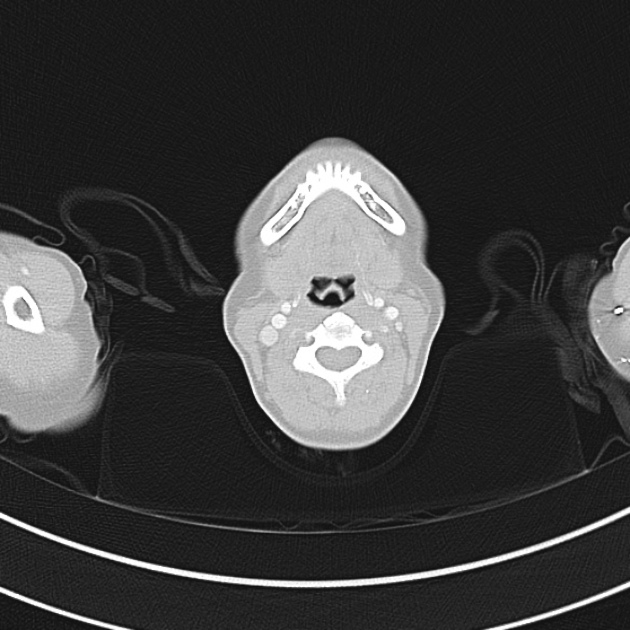
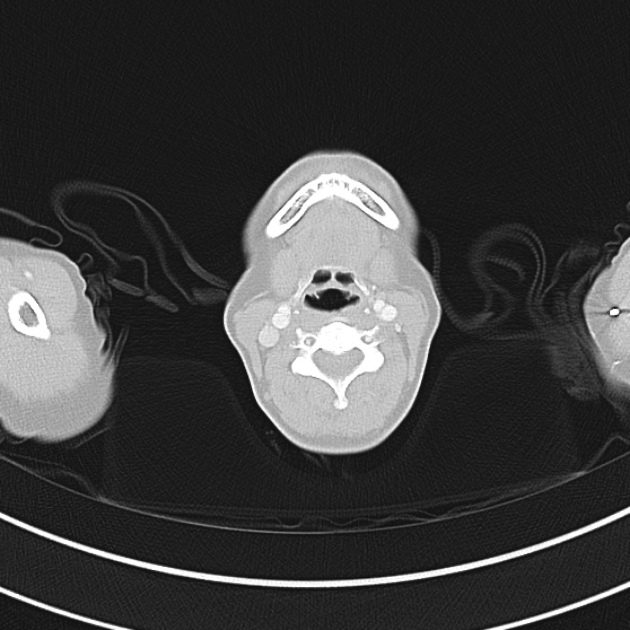
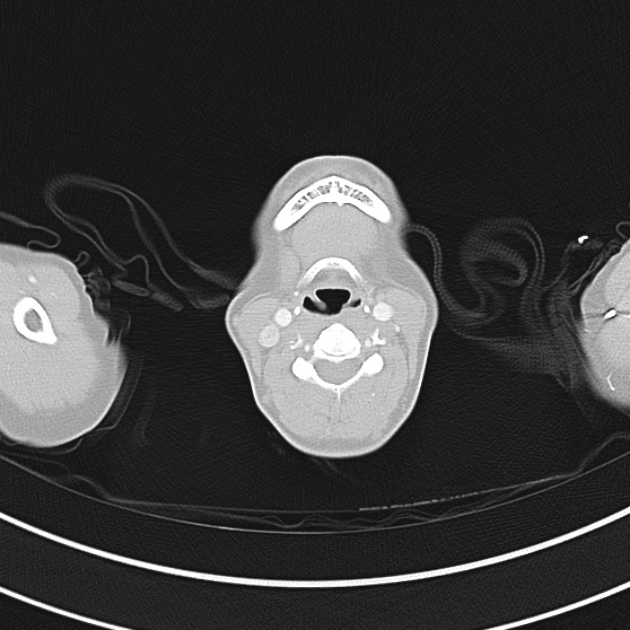
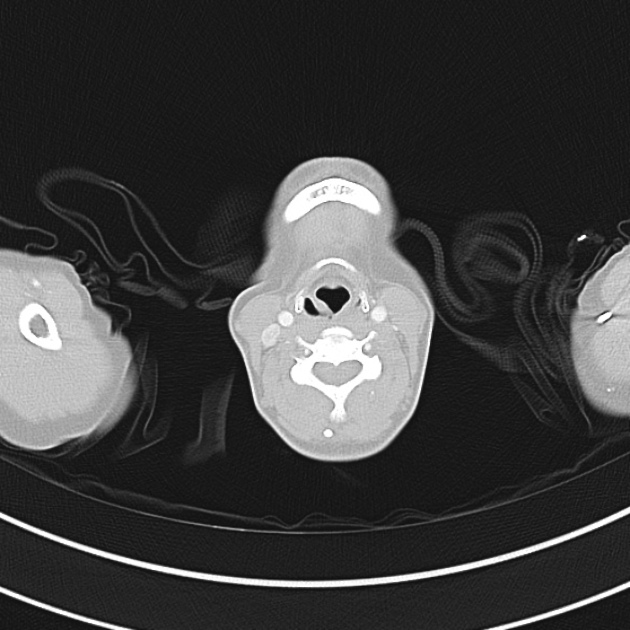
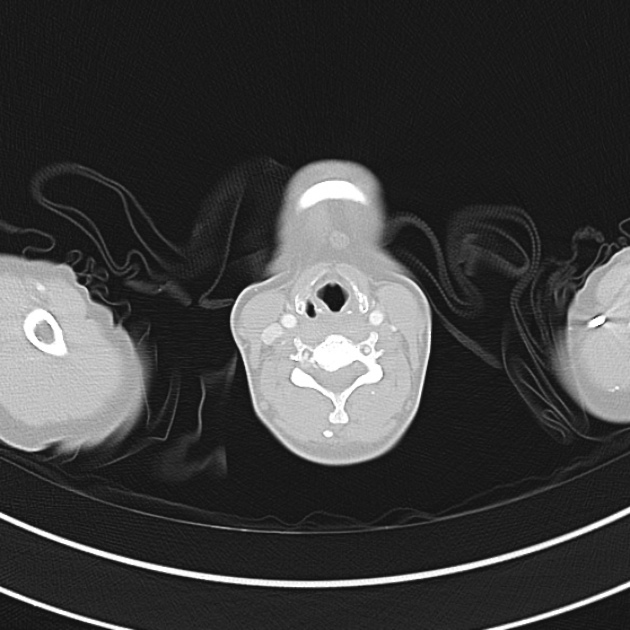
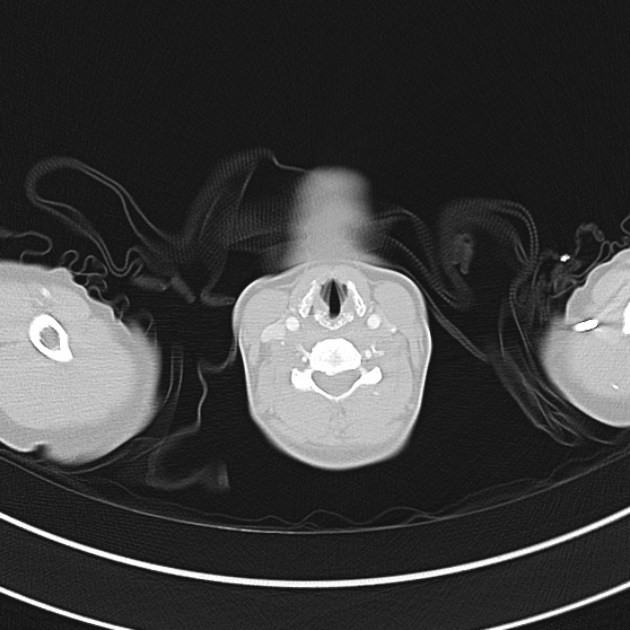
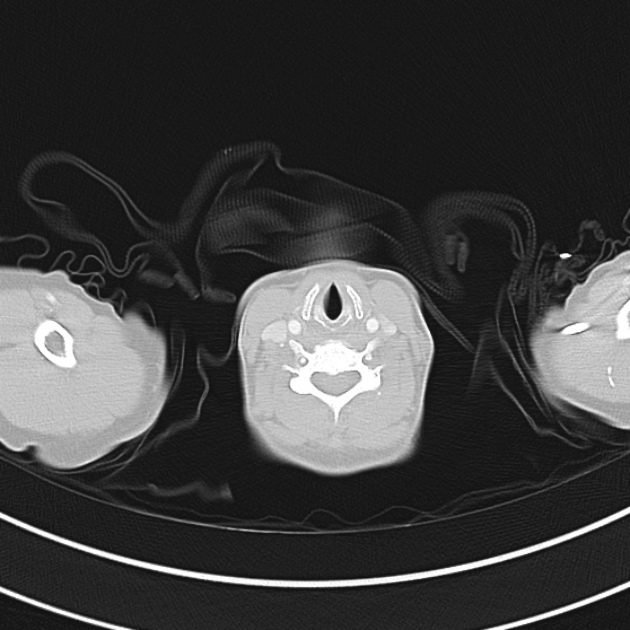
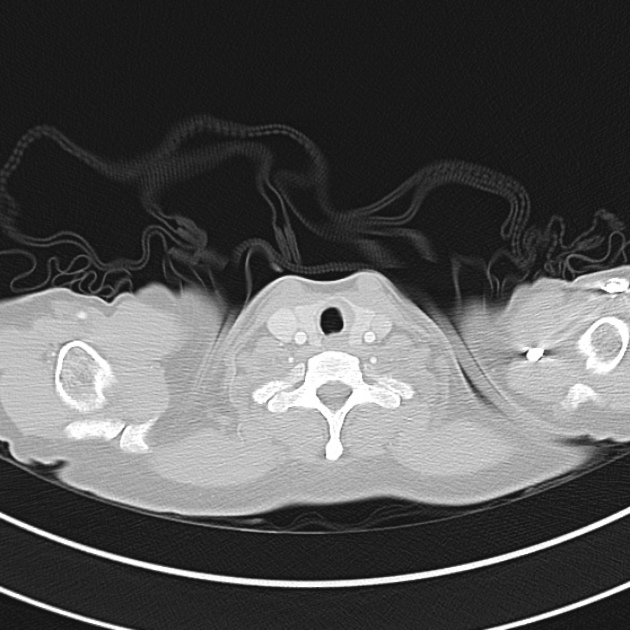
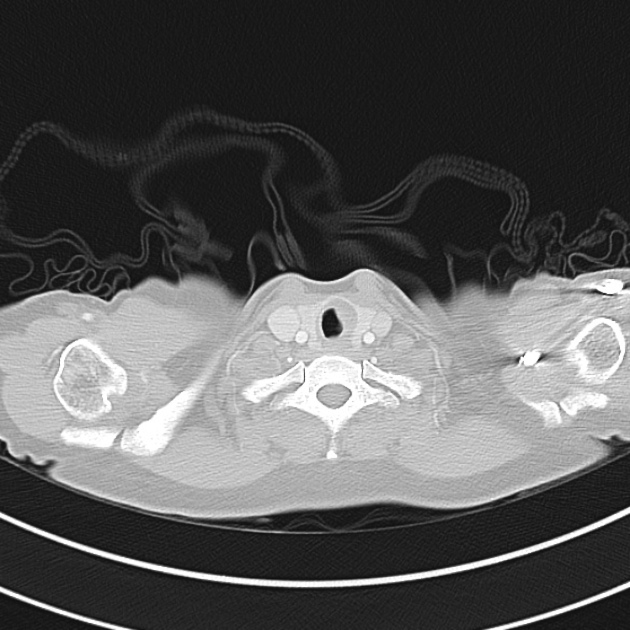
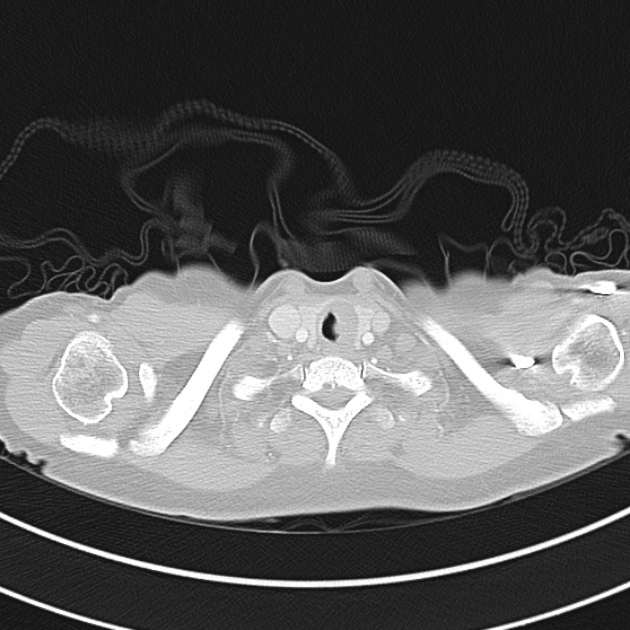
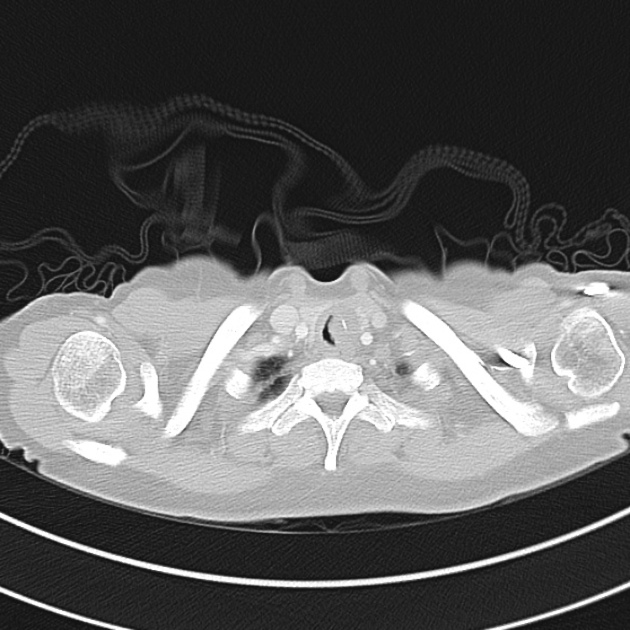
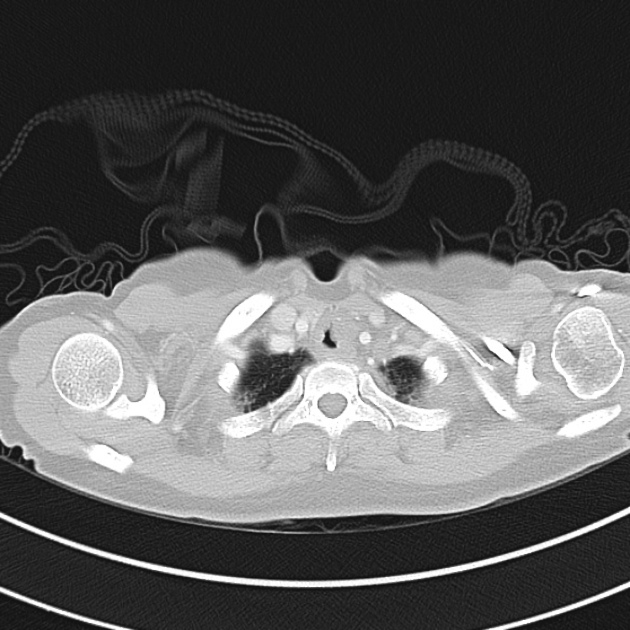
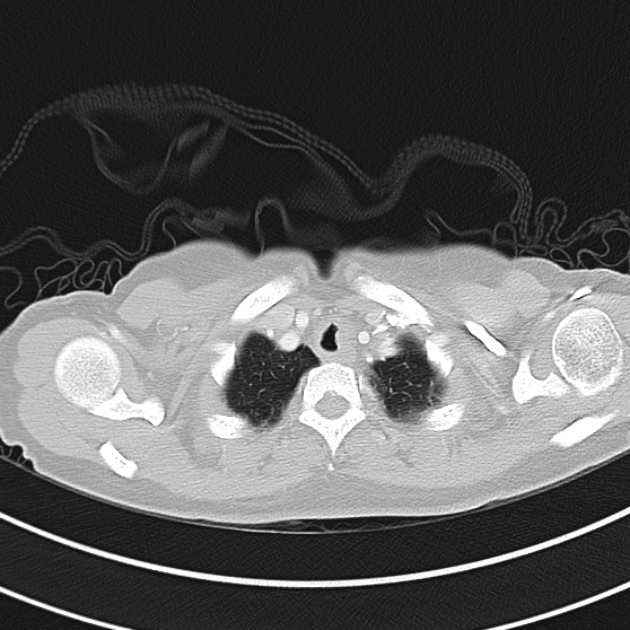
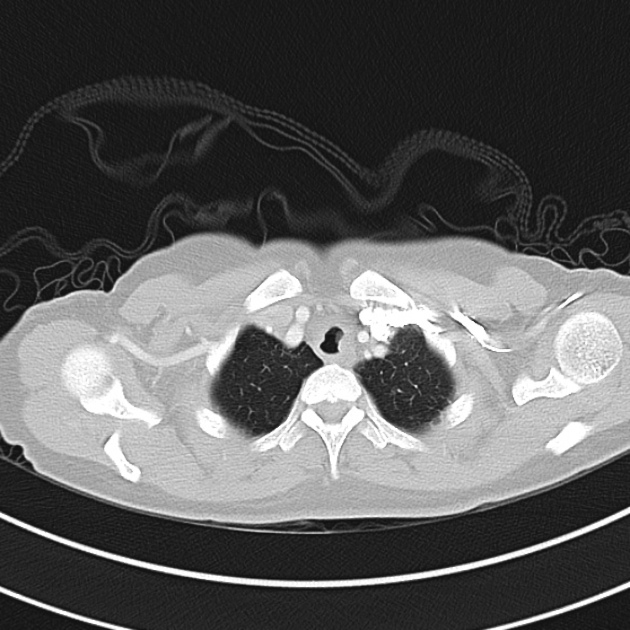
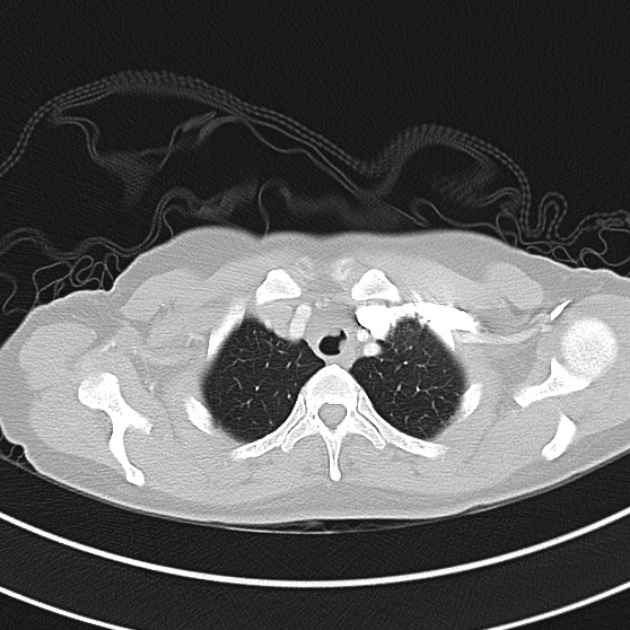
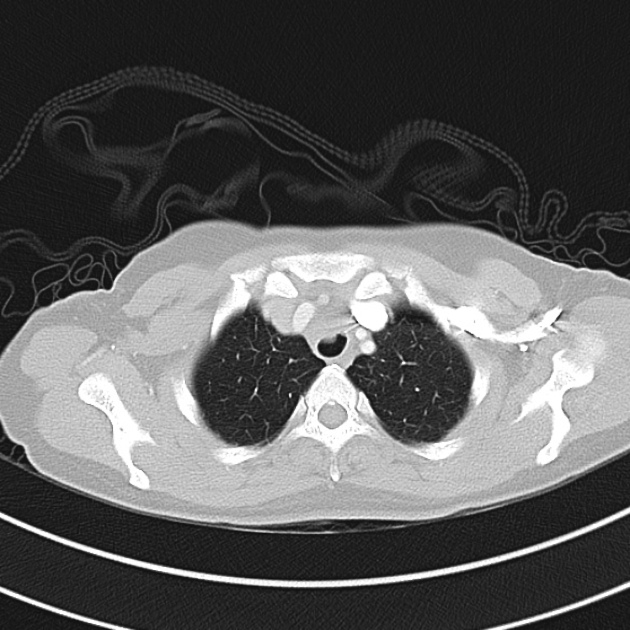
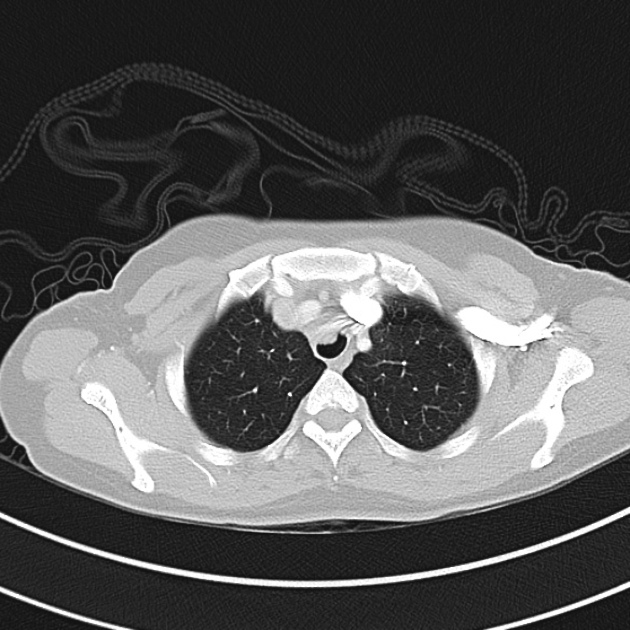
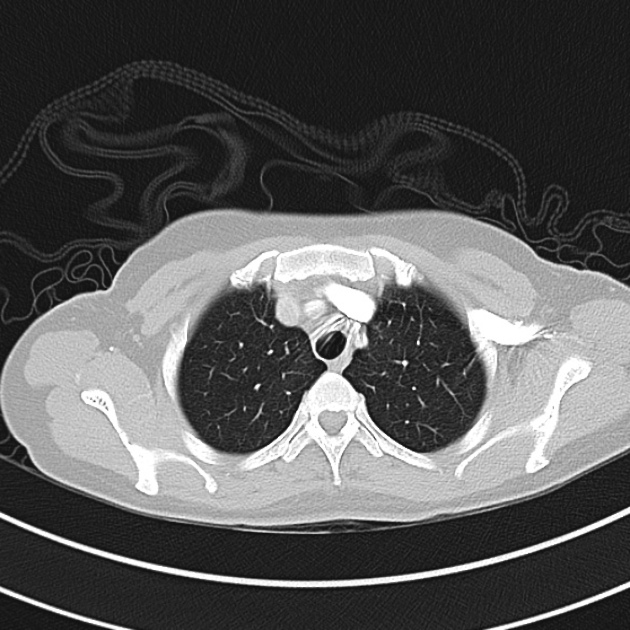
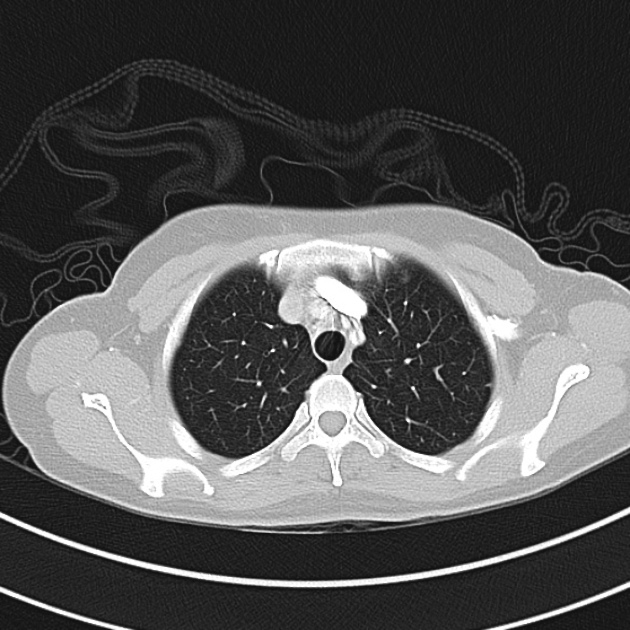
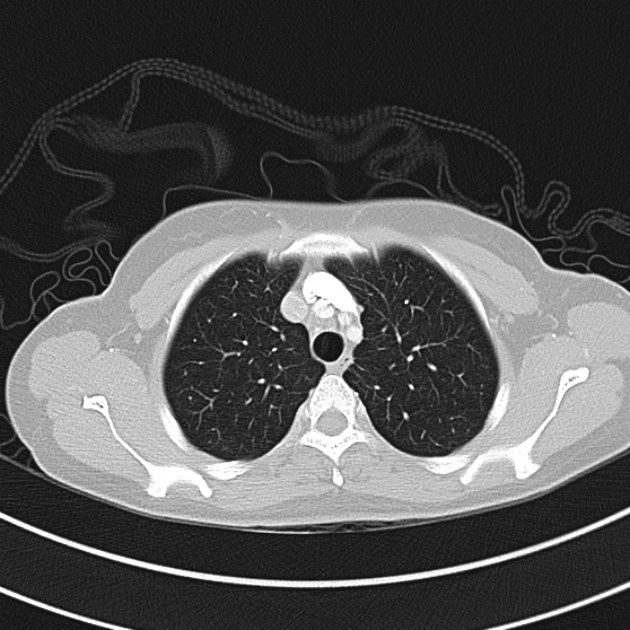
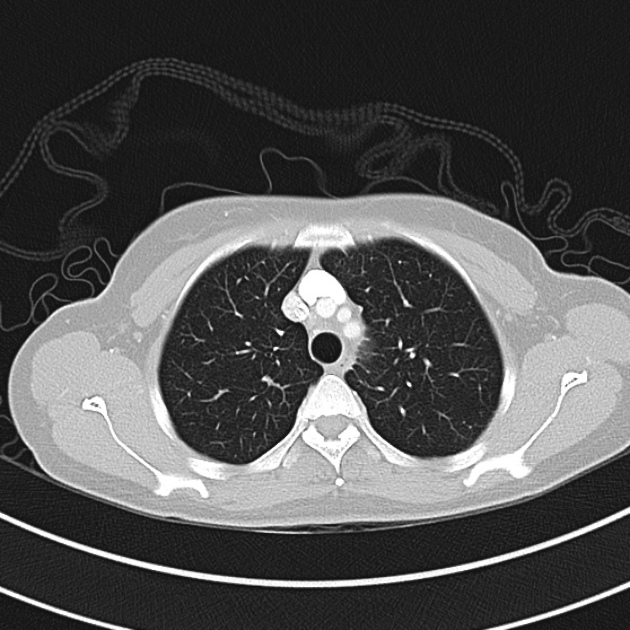
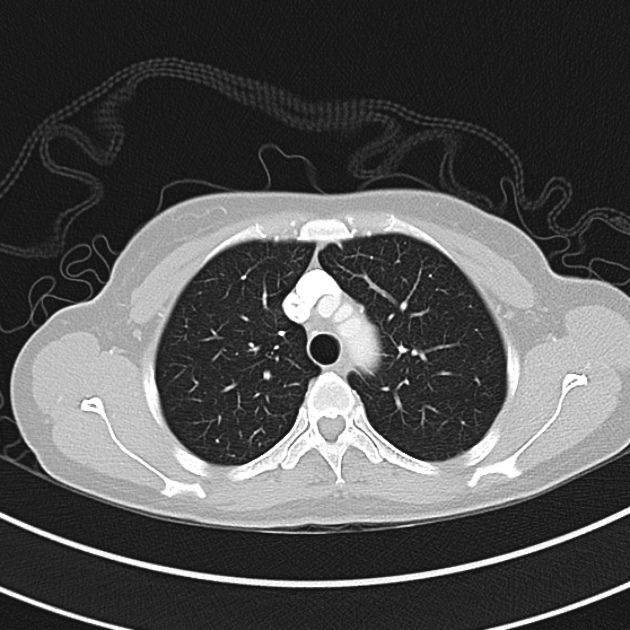
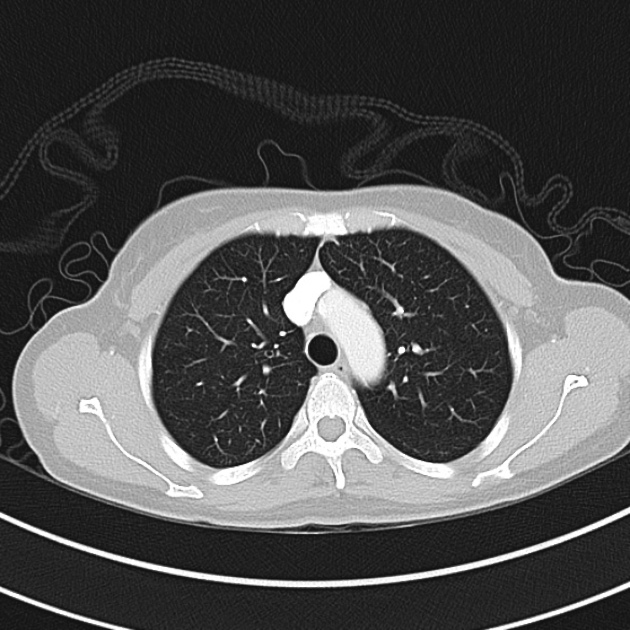
1.9cm soft tissue thickening of the left tracheal wall at the level of the inferior thyroid gland. Luminal narrowing to 4 mm at this level.
Case courtesy of Dr Ian Bickle from Radiopaedia.org: 47677
Sound Characteristics
Stridor
An inspiratory, expiratory, or continuous monophonic sound that is loudest over the central airways.
Wheezing
A musical, high-pitched sound – more commonly expiratory. Requires sufficient airflow to induce airway oscillations.
Respiratory Phase
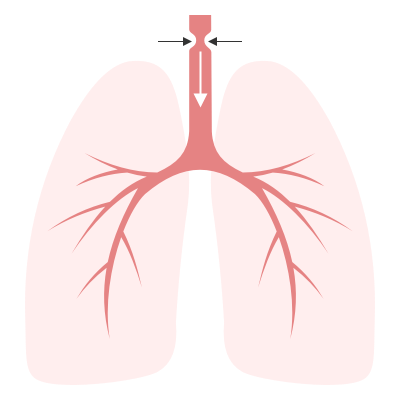
Inspiratory
Supraglottic: negative intratracheal pressure during inspiration causes airway collapse.
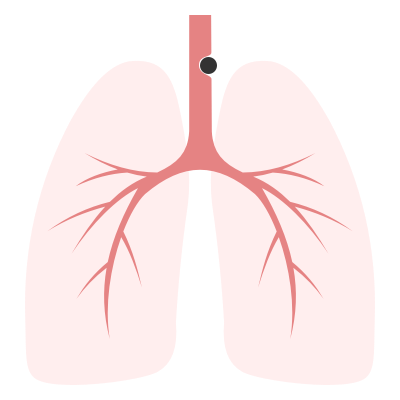
Biphasic
Glottic/Subglottic: fixed obstruction not impacted by changes in luminal/thoracic pressure.
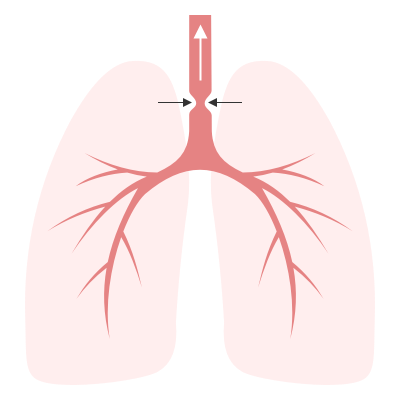
Expiratory
Intrathoracic: increased pleural pressure compresses the narrowed airway.
An Algorithm for the Diagnosis of Wheezing and Stridor
References
- Sicari V, Zabbo CP. Stridor. [Updated 2021 Jul 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525995/
- Patel PH, Mirabile VS, Sharma S. Wheezing. [Updated 2021 May 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK482454/
- Bohadana A, Izbicki G, Kraman SS. Fundamentals of lung auscultation. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(21):2053.
- Orient JM, Sapira JD. Sapira’s Art & Science of Bedside Diagnosis. 4th ed. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010.